
250+ Insider Threat Statistics for 2026
The team at Bright Defense has curated an exhaustive breakdown of over 250+ critical insider threat statistics for 2025. This guide serves as an evidence-based resource to help you understand the changing risks originating from within your own organization.
In this article, you’ll find hand-picked statistics about:
- Global Insider Threat Frequency and Prevalence
- Financial Impact of Insider Incidents
- Insider Risk Budgets and Program Maturity
- Remote and Hybrid Work Insider Risk
- Credential Theft, Phishing, and Human Error
- GenAI and AI-Enabled Insider Threats
- Extortion, Ransomware, and Insider Collusion
- Industry-Specific Insider Risk Exposure
- Insider Threat Motives and High-Risk Roles
- Notable Insider Breaches and Case Studies
[Note: These statistics were carefully handpicked from the world’s leading cybersecurity research platforms, such as IBM, Verizon, Ponemon, Mandiant, Fortinet, and many more, making the Insider Threat Stat article an authoritative and trustworthy research piece you can cite and use in business decisions]
Global Insider Threat Trends

- 76% organizations said insider attacks had become more frequent over the past year. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- The share of organizations experiencing insider attacks rose from 66% in 2019 to 76% in 2024. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
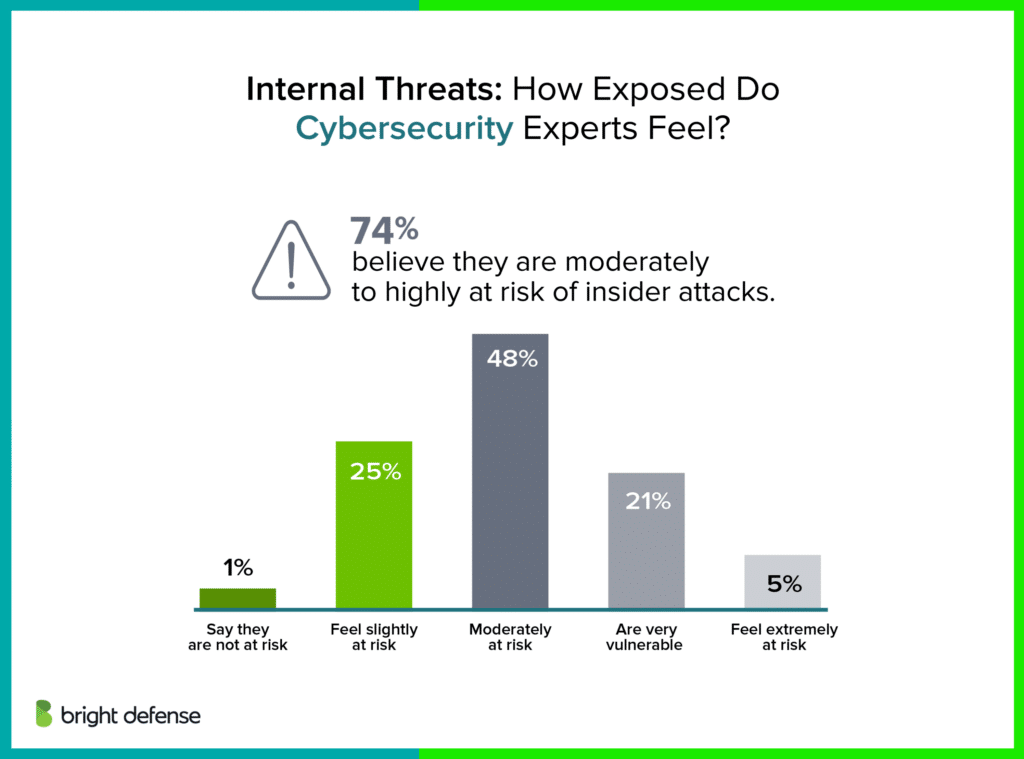
- 71% of organizations consider themselves at least moderately vulnerable to insider threats. (Syteca)
- 67% of companies experienced 21 to 40 insider threat incidents in 2022.
- That figure rose to 71% in 2023, indicating that insider threat incidents are increasing year over year. (Infosecurity Magazine, Station X)
- 28% growth in insider‑driven data exposure was reported between 2023 and 2024. (Station X)
- From 2020 to 2022, there was a 44% increase in the number of insider incidents. (Station X)
- Ponemon recorded 7,868 insider incidents in its 2025 study, more than double the 3,269 incidents examined in 2018. (Ponemon)
- Non‑malicious insiders accounted for 75% of incidents in the Ponemon 2025 study, with negligent employees causing 55% of events and external exploitation of employees causing another 20%. (Secureframe)
- Malicious insiders made up 25% of incidents in Ponemon’s data. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Credential theft accounted for 20% of insider incidents. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Organizations reported an average of 13.5 negligent insider incidents per organization in 2025. (Syteca)
- Each organization experienced about 6.3 malicious insider events on average. (Syteca)
- 50% of data breach detection in 2025 came from internal security teams, up from 42% in 2024 and 33% in 2023. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- 90% of respondents said insider attacks are as difficult or more difficult to detect than external attacks. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 93% of security professionals view insider threats as difficult or harder to detect than external breaches. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- Only 23% felt strongly confident in detecting insider risk events. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 8% of respondents were extremely confident in their detection capabilities. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 66% of respondents believe that a significant portion of their workforce could become susceptible to insider compromise under stress. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 52% of respondents think that 11 %–25 % of their workforce could be influenced into becoming an insider risk. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 68% believe that more than 10 % of employees would be susceptible to insider schemes. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 56% of organizations reported experiencing an insider threat incident in the past year (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- 64% of organizations reported having an established insider threat defense program (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- 97% of security professionals said they are concerned about negligent insider threats (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- 93% of security professionals said they are concerned about malicious insider threats (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- 87% of respondents said collaboration with HR or recruiting is part of their insider threat defense strategy. (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- About 60% of respondents said HR and security coordination is handled via informal chats, ad hoc emails, or manual ticket creation, with no automated workflows linking HR and security systems. (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- 67% of security teams said they are making it a priority to augment their insider threat detection and mitigation program in the next 12 months. (SpyCloud Insider Threat Pulse Report 2025).
- System intrusion, lost and stolen assets, and social engineering accounted for 76% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- Personal data appeared in 38% of breaches, other data in 35%, credentials in 33%, and internal data in 32%. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- 54% of organizations are using AI to detect insider risk. (Secureframe)
- 70% of those using AI cite reduced response times as a key benefit. (Secureframe)

The Rising Financial Cost of Insider Threats
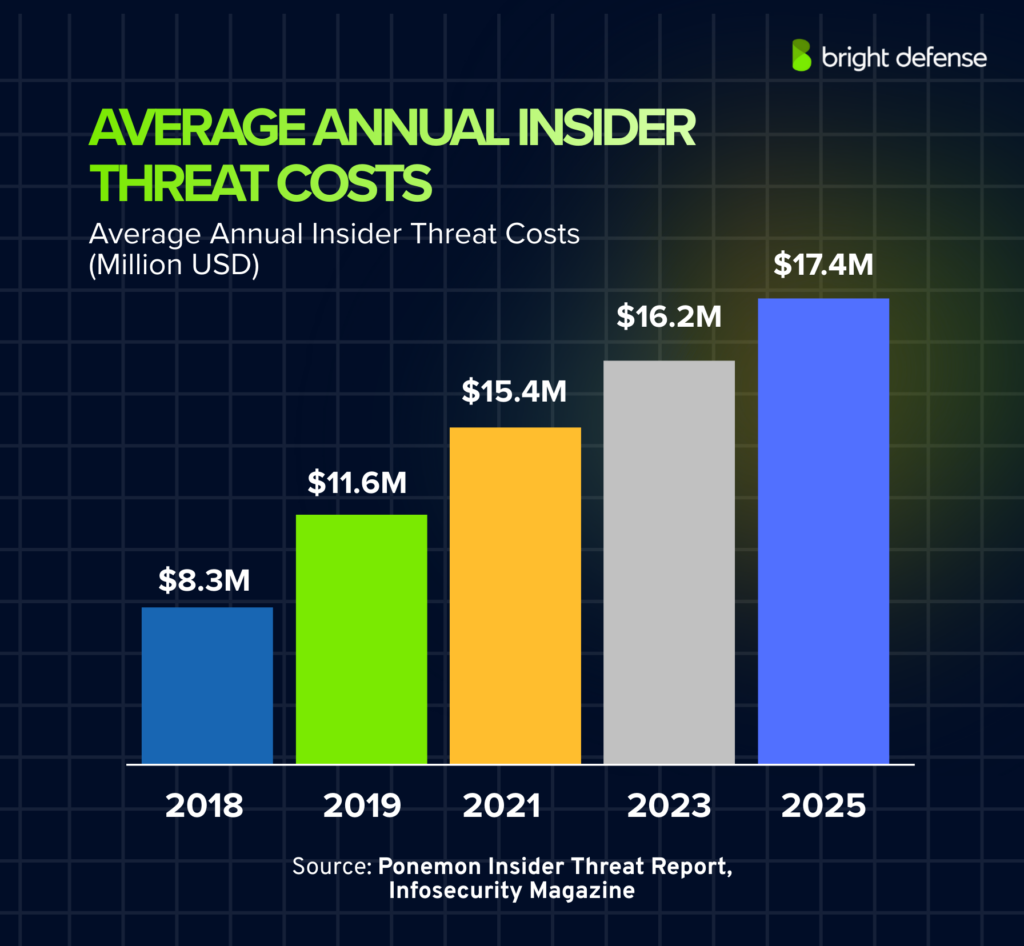
- Average annual cost of insider threats:
- 2018: $8.3M
- 2019: $11.6M
- 2021: $15.4M
- 2023: $16.2M
- 2025: $17.4M
The average annual insider threat cost increased by approximately 109.6% from 2018 to 2025.
(Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025, Infosecurity Magazine)
- North America spent $22.2 M on insider risk incidents in 2025. (Ponemon.org)
- Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) spent $20.3 M on insider risk incidents. (Ponemon.org)
- Average cost for North American organizations rose from $11.1 M in 2018 to $22.2 M in 2024. (Syteca)
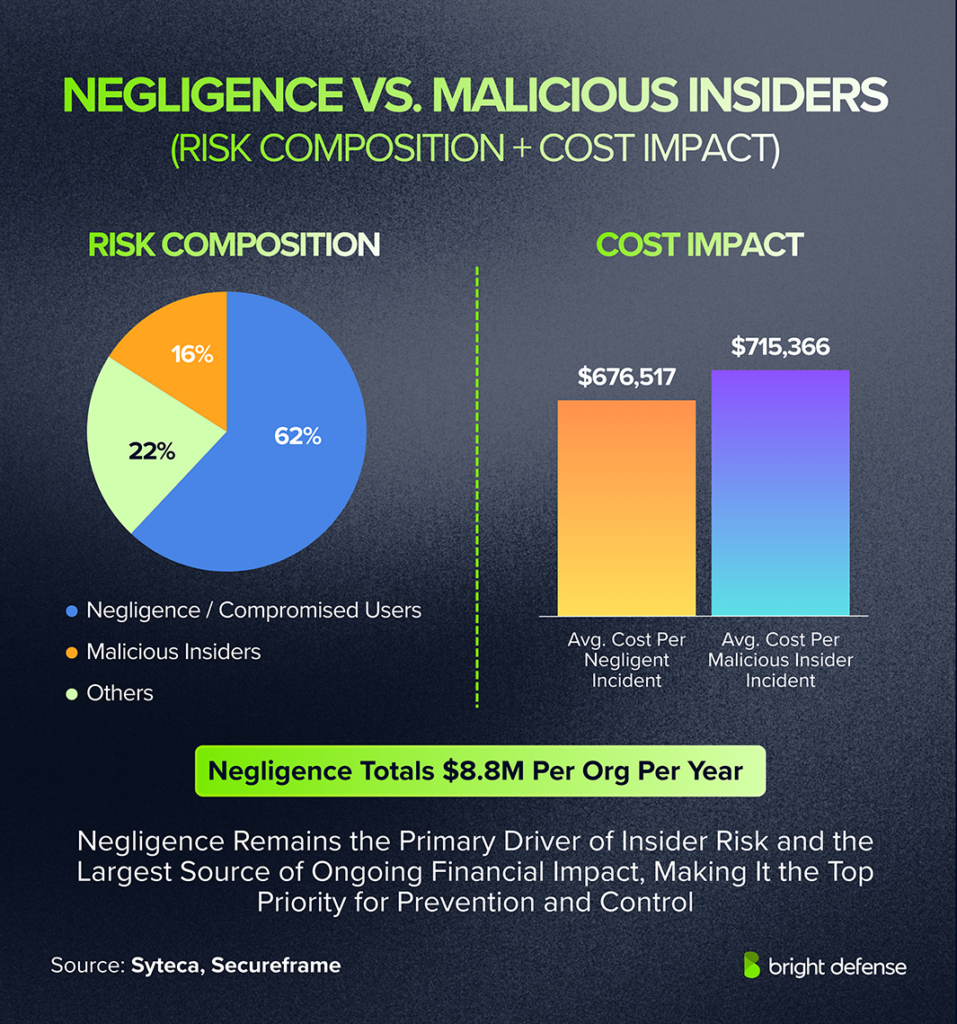
- 62% of insider incidents were attributed to negligence or compromised users and 16% to malicious insiders. (Secureframe)
- The cost per negligent incident averaged $676,517. (Syteca)
- The total annual cost for negligence was $8.8 M per organization. (Syteca)
- Malicious insider events cost $715,366 per incident. (Syteca)
- Ponemon found that each insider incident cost $211,021 on containment compared with $37,756 spent on monitoring. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Incidents contained in less than 31 days cost an average of $10.6 M. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Incidents contained after more than 91 days cost $18.7 M on average. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Incidents contained in more than 90 days cost $18.33 M, compared with $11.92 M for incidents contained in less than 30 days. (Station X)
- The average detection and containment time for insider incidents was 81 days in 2025, down from 86 days in 2023. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- The previous Ponemon report noted an average containment time of 85 days in 2021. (Infosecurity Magazine)
- Incidents taking more than 90 days to contain cost $17.19 M in the 2022 Ponemon analysis. (Proofpoint)
- Organizations with more than 75,000 employees spend about $24.6 M on insider incidents. (Station X)
- Organizations with fewer than 500 employees spend about $8M on insider incidents. (Station X)
- A large company with 25,001–75,000 employees spends about $26.2 M on insider risk events. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- In 2025, malicious insider incidents carried the highest financial impact, with an average breach cost of $4.92M, exceeding the $4.44M global average cost of a data breach. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Data breaches caused by compromised credentials cost $4.67 M on average. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- When an insider threat was the cause, organizations faced average containment costs of $211,021 per incident along with an additional $37,756 in monitoring costs. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Incidents lasting more than 91 days cost $18.7 M. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 16.5% of IT budgets were allocated to insider risk management. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Incidents contained within 31 days cost $10.6 M. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Budgets per employee averaged $402 for insider risk. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 81% of organizations report that insider risk programs saved time responding to incidents. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 63% said their insider risk program saved costs by reducing time to respond. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 45% of organizations believed their funding for insider risk was insufficient. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 72% of organizations reported that their budgets for insider risk or data protection are increasing. (Secureframe)
How Organizations Fund Insider Threat Programs

- 45% of organizations felt their insider risk funding was not adequate. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- Organizations devoted 16.5% of their IT budgets to insider risk management. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- In 2025, most organizations remained in early insider risk maturity, with 51% at Level 2, 25% at Level 1, 18% at Level 3, and 6% still at Level 0. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
[ Note: Insider risk maturity levels describe how well an organization understands, manages, and reduces insider threats
- Level 0: No formal insider risk program or visibility.
- Level 1: Reactive, ad hoc response to incidents.
- Level 2: Defined processes with limited tools and visibility.
- Level 3: Formal governance and consistent monitoring.
- Level 4: Proactive, intelligence-driven insider risk management. ]
- Only 14% felt fully confident in their ability to detect insider data loss. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 64% had a formal data protection program, but 51% said their tools were fragmented. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 72% of organizations report that their insider risk budgets are increasing. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 27% saw significant budget growth, 45% saw moderate increases, 19% saw no change, and 4% saw decreases. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 8.2% of total security budgets were spent on insider risk programs. (Station X)
- 38% of organizations place insider risk responsibilities within the Security or SOC team. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 26% assign these duties to data protection teams. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 12% have a dedicated insider risk group. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)

Extortion and Ransom Patterns Linked to Insider Threats

- Payment dynamics cover extortion demands and decisions to pay or refuse.
- In Coinbase’s 2025 case, attackers bribed customer support agents and demanded a $20M ransom. (Helpnet Security)
- Coinbase refused to pay the ransom and instead offered a $20M reward for information leading to the criminals’ arrest. (Helpnet Security)
- The extortionists accessed data on 69,461 users, which Coinbase said represented less than 1% of its monthly active users. (Helpnet Security)
- A separate IBM study found that 63% of organizations refused to pay ransom demands in 2025. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Extortion‑related breaches cost $5.08 M on average. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- 97% of organizations lacked proper AI access controls at the time of a breach, illustrating vulnerabilities that can be exploited in ransom demands. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- 16% of data breaches involved AI‑driven attacks in 2025. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- AI‑driven phishing campaigns were present in 37% of AI‑related breaches. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Deepfake impersonation appeared in 35% of AI‑related breaches. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
Ransomware and Organized Groups Linked to Insider Threats
- Mandiant observed that 5% of initial infection vectors in 2024 were due to insider threats, an increase driven largely by North Korean IT workers (UNC5267) posing as legitimate job applicants. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- In M‑Trends 2025, exploitation of vulnerabilities accounted for 33% of initial infection vectors. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Malware families tracked by Mandiant exceeded 5,500 in total, with 632 families newly tracked in 2024. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Mandiant M Trends reports that 69% of tracked malware families targeted Windows operating systems, 26% focused on Linux systems, and 5% targeted other platforms such as network devices and mobile environments. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Financial sector investigations made up 17% of Mandiant’s cases in 2024. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Healthcare investigations accounted for 15%. (Mandiant – M Trends).
- Technology sector investigations were 11% of the total. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Professional services accounted for 10% and manufacturing for 8%. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- The global median dwell time in Mandiant’s investigations increased to 11 days from 10 days in 2023. (Mandiant – M Trends)
Motives Behind Insider Threat Activity
- Frustration over financial payouts can create resentment that erodes judgment, making misuse of trusted access feel justified and increasing the likelihood of malicious insider incidents. A staggering 89% of malicious insider breaches were motivated by financial gain.
- 13% were driven by personal grudges.
- 5% were due to espionage.
- 3% were related to convenience.
- 3% occurred for fun.
- 2% were ideological. (Station X)
- 74% of security professionals said they were most concerned about malicious insiders. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 37% of leaders cited insufficient employee training as a top driver for insider incidents. (Station X)
- 34% cited new technologies as a risk factor. (Station X)
- 29% cited inadequate security measures. (Station X)
- 27% pointed to complex IT environments. (Station X)
- 25% cited disgruntled insiders as a primary concern. (Station X)
- 81% of security leaders considered senior managers the greatest threat to data security. (Station X)
- 83% of breaches were driven by external actors, most classified as organized cybercriminal groups, while 19% involved internal actors. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- Ransomware appeared in 62% of incidents tied to organized crime groups, making it the most common attack method used by these groups. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- 59% of all financially motivated cyber incidents involved ransomware, reinforcing its role as the primary tool for organized groups. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- Collusion between insiders and external criminals increased sharply in 2023, especially in fraud and ransomware related cases. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- Dark web recruitment of corporate insiders rose steadily from 2019 to 2024, with sharp growth in telecom, tech, and e-commerce sectors. (Nisos, Insider Threat Activity Report, Jan 2025)
- Real cases show ransomware groups attempting to recruit employees as accomplices. In 2023 to 2024, the Medusa ransomware group contacted a BBC employee and offered 15% of any ransom payment for help gaining network access. The incident, revealed by a BBC journalist, shows how organized groups use financial incentives to pressure insiders into assisting attacks. (Coveware)
- Only 17% of organizations reported zero insider incidents in 2024, down from 40% in 2023, while reports of 11–20 insider incidents rose to 21%. (Cybersecurity Insiders, Insider Threat Report 2024)
Insider Threats Involving Stolen Credentials and Phishing

- 45% of human error breaches involve sending data to the wrong recipient. (Station X)
- Misdelivery accounts for 72% of internal action types in Verizon’s DBIR 2025. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- End‑users made up 9% of actor varieties in internal breaches. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- 88% of breaches are made worse by employee mistakes. (Station X)
- 55% of insider incidents result from negligence. (Station X)
- 43% of misdelivery errors occur when data is sent to the wrong recipients. (Station X)
- 89% of personal data compromised in insider-related error breaches is of personal nature. (Station X)
- 44% of finance sector breaches were internal, and 55% of those involved misdelivery. (Station X)
- 25% of employees admitted to clicking on phishing emails. (Station X)
- 34% of men clicked on phishing links compared with 17% of women. (Station X)
- 45% of employees who clicked blamed distraction for their action. (Station X)
- 43% said the email looked legitimate. (Station X)
- 41% said the email came from an executive or someone in authority. (Station X)
- 43% of U.S. adults share passwords with a partner or friend. (Station X)
- 53% of IT professionals admit to sending passwords through email. (Station X)
- The password “123456” appeared 33 times among the most common credentials breached. (Station X)
- AI‑augmented credential abuse was a top concern for 53% of security leaders. (Secureframe)
- Automated data exfiltration using AI worried 61% of security leaders. (Secureframe)
- AI‑facilitated phishing and deepfake social engineering worried 69% of respondents. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Remote Work and Device Risks in Insider Threat Cases

- 75% of security professionals identified the remote or hybrid workforce as their biggest emerging insider risk. (Secureframe)
- 70% of cyber professionals were concerned about insider risk in hybrid workplaces. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 12.7% of U.S. employees worked remotely in 2023, and this is expected to rise to 22 % by 2025. (Station X)
- 91% of executives believe that insider attacks increased due to remote work. (Station X)
- 57% of remote employees said they were more distracted while working remotely. (Station X)
- 72% of organizations lack full visibility into how employees interact with sensitive data. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- Only 28% of organizations have effective data discovery and classification. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 56% of security leaders were concerned about employees sharing sensitive data with generative AI tools such as ChatGPT. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- Only 12% of organizations felt prepared to address risks from ChatGPT. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 47% strongly agreed that their data loss prevention (DLP) tools were effective. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 72% of budgets for insider risk or data protection are rising. (Secureframe)
- 27% of organizations noted significant budget increases for insider risk programs. (Secureframe)
- 69% said budgets are increasing moderately. (Secureframe)
- 72% cite business and IT complexity as the principal driver for insider risk. (Secureframe)
- 71% of respondents reported inadequate tools as a barrier to effective insider risk management. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 69% cited insufficient budgets as a barrier. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 58% identified privacy concerns as a challenge. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Initial Access Paths and Tactics in Insider Threat Incidents
- Misdelivery accounted for 72% of internal action varieties. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- Privilege misuse actions occurred half as often as miscellaneous errors, giving a ratio of roughly 1:2. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- End users were involved in 9% of actor categories in internal incidents. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- Espionage‑motivated breaches increased by 163% in Verizon’s dataset. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- 43% of human error breaches were due to employees sending information to the wrong recipients. (Station X)
- 45% of employees who clicked phishing links cited being distracted. (Station X)
- 25% of incidents were caused by malicious insiders with intent. (Station X)
- 62% of insider incidents were attributed to negligent or compromised users. (Secureframe)
- Only 16% of incidents involved malicious intent. (Secureframe)
- 21% of organizations reported more than 20 insider incidents in the past 18 months. (Secureframe)
- 41% of organizations said their most serious insider incident cost between $1 M and $10 M. (Secureframe)
- 73% of security professionals reported being most concerned about negligent employees. (Secureframe)
- 62% were concerned about individuals handling sensitive data. (Secureframe)
- 55% were concerned about departing employees. (Secureframe)
- 76% of respondents linked the rise of insider risk to increasing IT complexity. (Secureframe)
- 53% of respondents expected sophisticated social engineering campaigns to increase. (Secureframe)
- Only 21% of organizations have fully implemented insider risk programs. (Secureframe)
- 69% of organizations rely on informal processes to handle insider incidents. (Secureframe)
Industry Impacts of Insider Threat Activity
- Financial services organizations experienced 20.68M USD average insider incident cost in Ponemon’s 2023 study. (Station X)
- 17% of Mandiant investigations in 2024 involved the financial sector. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- 44% of finance‑related breaches were caused by insiders. (Station X)
- 55% of these finance insider incidents were due to misdelivery. (Station X)
- Finance had 99 non‑malicious insider actions in Verizon’s data. (Station X)
- Finance had 40 malicious insider actions. (Station X)
- Finance had an insider breach cost of $701,500 for malicious events. (Station X)
- Credential theft incidents in finance cost $679,621 on average. (Station X)
- The average cost to contain an insider incident in finance was $179,209. (Station X)
- North American financial institutions spent $24.6 M on insider incidents in organizations with more than 75k employees. (Station X)
- Manufacturing represented 8% of Mandiant investigations in 2024 (Mandiant – M Trends)
- The technology sector accounted for 11% of Mandiant’s investigations in 2024. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- In Verizon’s dataset, the information sector had 89 non‑malicious insider actions. (Verizon DBIR 2023)
- Information sector logged 21 malicious insider actions. (Station X)
- Professional services comprised 10% of Mandiant investigations. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Many professional services firms outsource IT, increasing reliance on third‑party vendors; 77% of respondents considered vendors a high‑risk role for insider abuse(Cybersecurity Insiders).
- The education sector had 51 non‑malicious insider actions in Verizon’s data. (Station X)
Insider Threat Risks in Healthcare
- Healthcare made up 15% of Mandiant investigations in 2024. (Mandiant – M Trends)
- Verizon noted 141 non‑malicious insider actions in the healthcare sector. (Station X)
- Healthcare recorded 65 malicious insider actions. (Station X)
- In malicious insider breaches, medical information was compromised in 34% of cases. (Station X)
- Personal data was compromised in 73% of malicious insider incidents, with 34% involving medical data. (Station X)
- Banks and payment data were compromised in 12% of malicious incidents. (Station X)
- 18% of data in malicious incidents fell into “other” categories. (Station X)
- 73% of personal data exposures in insider cases were of personally identifiable information. (Station X)
- According to Fortinet, 62% of security professionals are concerned about individuals handling sensitive data such as medical records. (Secureframe)
Insider Threat Exposure in Public Administration
- Public administration had 2,069 non‑malicious insider actions in Verizon’s dataset. (Station X)
- Public administration logged 16 malicious insider actions. (Station X)
- Government entities are frequent targets for espionage, as indicated by the 163% increase in espionage‑motivated breaches. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
- Several high‑profile public sector incidents involve insider misuse of email for misdelivery. (Verizon DBIR – 2025)
Regional and Country-Level Insider Threat Data
- North American organizations faced average insider incident costs of $22.2M in 2025. (Ponemon.org)
- The U.S. had the highest average data breach costs at $10.22 M. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- The global average breach cost was $4.44 M, less than half of the U.S. figure. (IBM – Cost of a Data Breach Report)
Cost Impact and Recovery Patterns from Insider Threats

- 65% reported that the program prevented a breach. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- 38% of organizations placed insider risk responsibilities in the security or SOC team. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 26% assigned the function to data protection. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 12% created a dedicated insider risk team. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 51% of organizations were at Level 2 maturity for insider risk, 25% at Level 1, 18% at Level 3, and 6% at Level 0. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 27% said budgets were growing significantly. (Secureframe)
- 19% said budgets were unchanged. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 4% reported declining budgets. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 69% of organizations rely on informal approaches for insider risk management. (Secureframe)
- Only 27% have a formal response plan. (Secureframe)
- 72% cannot see how users interact with sensitive data. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 28% have effective data discovery and classification. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 66% prioritize real‑time behavioural analytics to address insider risk. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 52% prioritize controls for SaaS and generative AI tools. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 47% strongly believe data loss prevention solutions are effective. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 64% have a formal data protection program. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
- 51% said their tools for data protection are fragmented. (Fortinet – Insider Risk Report 2025)
Human Impact of Insider Threats on Security Teams
- 90% of security professionals said insider attacks are as challenging or more challenging than external attacks. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 74% of respondents were most concerned about malicious insiders. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- Only 16 % considered themselves extremely effective at deterring insider threats. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 41% said their organization has only partially implemented an insider threat program(Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 29% felt fully equipped with the right tools to handle insider threats. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 70% were concerned about insider risk in hybrid work environments. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 75% were concerned about emerging technologies such as AI, the Metaverse, and quantum computing. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 76% reported ransomware or triple‑extortion attacks had increased the risk posed by insiders. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 56% of respondents were concerned about information disclosure. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 48% were concerned about unauthorized data operations. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 41% had only partially implemented insider risk programs. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- 66% of respondents feel vulnerable to insider attacks. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- Only 21% of organizations fully use behavioural indicators such as HR signals and financial stress for insider risk detection. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- Only 12% have mature predictive models for insider risk. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 83% of respondents identified IT administrators as the highest‑risk role for insider threats. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 77% viewed third‑party vendors as high risk. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 64% viewed executives as high risk. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 49% of organizations found insider data on the dark web. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 43% said insider attacks are more challenging than external attacks. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 50% said insider attacks are equally challenging as external attacks. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 7% said insider attacks are less challenging. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 2% believed their workforce is resistant to insider risk. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 52% of respondents said 11%–25% of employees could be influenced by malicious actors. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 68% think more than 1 in 10 employees would be susceptible to insider schemes. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- 60% of security leaders are highly concerned about employees misusing AI tools for insider breaches. (Secureframe)
- 61% worry about AI enabling automated data exfiltration. (Secureframe)
- 53% worry about AI‑assisted credential abuse. (Secureframe)
- 69% worry about AI‑facilitated phishing and deepfake attacks. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
How Insider Threat Risk Has Changed Over Time
- The number of insider incidents studied increased from 3,269 in 2018 to 7,868 in 2025. (Ponemon.org)
- The average containment time increased from 77 days in 2020 to 85 days in 2021. (Infosecurity Magazine)
- It decreased to 81 days in 2025. (Ponemon Insider Threat Report – 2025)
- The share of organizations experiencing insider attacks rose from 66% in 2019 to 76% in 2024. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- The proportion of organizations feeling vulnerable to insider attacks increased from 68% in 2020 to 75% in 2024 (numbers derived from cross‑study comparison; 66% feel vulnerable in 2024, and 75% feel vulnerable in some other context. (Securonix – Insider Threat Report)
- The proportion of organizations relying on informal processes remained high at 69% in 2025. (Secureframe)
- There was a 34% increase in the cost of insider incidents between 2020 and 2021, from $11.5 M to $15.4 M. (Infosecurity Magazine)
- The number of companies experiencing 21–40 incidents rose from 60% in 2020 to 67% in 2022 and 71% in 2023. (Infosecurity Magazine)
- The average time to contain an incident increased from 77 days in 2020 to 85 days in 2021 and then fell to 81 days in 2025. (Infosecurity Magazine)
- The cost of credential theft incidents grew 65% from $2.79 M in 2020 to $4.6 M in 2022. (Proofpoint)
- 76% of organizations attributed the rise in insider risk to the complexity of IT systems in 2025. (Secureframe)
- 71% believed inadequate tools were a barrier to effective insider risk management in 2025. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
- The share of organizations fully confident in their ability to detect insider risk remained below 25% across the period. (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Notable Insider Threat Incidents
- In the Intel insider case, former employee Jinfeng Luo downloaded approximately 18,000 sensitive files just before termination. Intel’s data loss prevention (DLP) blocked one of Luo’s attempts but he used another device to exfiltrate data. Intel sought at least $250,000 in damages when it sued Luo for the theft. (eSecurity Planet)
- The Coinbase breach affected 69,461 users. Attackers demanded a $20 M ransom from Coinbase but the company refused. Coinbase offered a $20 M reward for information leading to the criminals’ capture. The attackers accessed names, addresses, phone numbers, last four digits of Social Security numbers, masked bank account numbers, identity document images, and some account balances. The affected users represented less than 1% of Coinbase’s monthly active user base. (Helpnet Security)
Liked the stat content? Check Out our latest stat articles:
Which Mitigation Strategies Can I Use to Prevent Insider Threats?
Insider threats hurt because trusted access already exists. So the best prevention play is to shrink standing access, then watch the small set of actions that actually cause damage.
The financial stakes are real: the 2025 Ponemon insider threat report puts the total average annual cost at $17.4M, and incidents that linger get far more expensive ($10.6M when contained under 31 days vs $18.7M when they run past 91 days). (Source: DTEX Systems)
Step 1: Define Your “High-Risk Actions” List (Start With 20)
Keep it short and concrete. Examples:
- Exporting large datasets from CRM, data lake, ticketing, or source control
- Changing MFA settings, adding new auth factors, creating API tokens
- Granting admin roles, changing IAM policies, disabling logging
- Bulk file downloads from Google Drive, SharePoint, Box, or Git repos
- Forwarding rules and mailbox delegation changes
If you can’t write it as a verb that shows up in logs, it is too vague.
Step 2: Remove Standing Privilege, Switch To Just-In-Time Access
For every high-risk action:
- Default access stays off.
- Users request elevated access for a short window (30 to 120 minutes).
- Approval routes to a manager plus a system owner for the first few months.
- MFA is mandatory, and device posture rules apply.
This matches the Zero Trust idea that no user account gets implicit trust just because it sits inside the network. (Source: NIST Computer Security Resource Center)
Practical tooling options:
- Cloud IAM plus Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Conditional access policies (location, device health, risk score)
- Short-lived tokens and session limits for admin consoles
Step 3: Put “Two-Person Control” On The Few Actions That Can End You
Use dual approval for:
- Disabling EDR
- Turning off audit logs
- Adding new IdP apps or changing SSO settings
- Large-scale permission grants
This is cheap friction with huge payoff.
Step 4: Monitor Only What Matters, And Respond Fast
Skip the noisy “watch everything” trap. Alert on:
- First-time access to a sensitive repo or dataset
- Bulk download spikes
- Access at odd hours for that user
- New forwarding rules, OAuth grants, or token creation
- Permission changes tied to the high-risk list
Government guidance stresses early intervention based on anomalous behavior signals, before major damage happens. (Source: Director of National Intelligence)
Step 5: Treat Offboarding and Role Changes as a Security Event
Same day actions:
- Kill sessions and revoke tokens
- Rotate shared secrets
- Transfer ownership of shared assets
- Review recent downloads and exports for the user and their closest peers
Why this technique beats “annual training” as your main control
Training helps, but standing access plus weak visibility still lets 1 bad moment turn into a breach. Time-bound privilege cuts blast radius. Targeted monitoring raises detection speed. Together, they reduce the chance that an insider can move fast and quietly.
How Bright Defense Can Help
Bright Defense helps prevent insider threats with services that reduce over-permissioned access, tighten control over sensitive actions, and prove your defenses work under real pressure.
A strong insider-risk program needs an informed workforce that knows what “concerning behavior” looks like and how to report it early. Bright Defense supports security awareness and insider-risk training that reinforces reporting culture, policy adherence, and real-world scenarios, helping reduce accidental and intentional insider risk. This aligns with federal guidance that treats insider-threat awareness training as a core component of an effective security program.
Our vCISO support gives you ongoing leadership to build and run an insider-risk program, covering access governance, policy, investigations, and response planning.
Continuous compliance keeps controls like least privilege, MFA enforcement, logging, and access reviews active year-round instead of only at audit time. If you need formal assurance, SOC 2 and ISO 27001 services strengthen insider-risk defenses through structured access control, change management, and monitoring expectations.
FAQ
Insider threats are a frequent and costly risk. Over 80% of organizations reported at least 1 insider-related incident in the past year, and nearly 50% say incidents are rising year over year. Negligence and credential misuse cause most cases.
The average annual cost exceeds $17M, with 80+ days to contain on average. Insider-driven breaches account for roughly 6% to 20% of confirmed breaches, especially in data-heavy sectors. While about 80% have insider risk programs, nearly 50% report insufficient funding, and insider risk takes about 15% to 17% of security budgets.
The “95%” claim usually refers to the human element contributing to incidents, including mistakes, manipulation, or misuse of access. IBM’s Cyber Security Intelligence Index linked 95%+ of investigated incidents to human error factors like misconfigurations, weak passwords, misdirected emails, and phishing clicks.
More conservative datasets vary: Verizon’s 2025 DBIR reports the human element in about 60% of confirmed breaches.
The 4 major data threats are commonly summarized as four broad categories of attacks on information systems, used in many security models to assess risk from both insiders and external threats:
1. Interception (Confidentiality breach)
An unauthorized party gains access to an asset, such as through wiretapping, packet sniffing, or illicit file copying.
2. Interruption (Availability loss)
An asset or service becomes unavailable or unusable, for example by destroying hardware, cutting communication lines, or disabling file services through denial-of-service attacks.
3. Modification (Integrity compromise)
An unauthorized party tampers with an asset, including changing database values, altering programs, or modifying messages in transit.
4. Fabrication (Authenticity and integrity deception)
An attacker inserts fake or illegitimate data or transactions, such as spoofed records or messages, counterfeit credentials, or falsified logs.
These categories align with confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and they also map cleanly to the tactics used by modern threat actors targeting high-value systems.
Most commonly, in the inbox through phishing emails. The “90%” claim points to many successful attacks starting when a user clicks a malicious link, opens an attachment, or shares credentials. That often leads to account takeover and broader access unless email security and user safeguards are strong.
If you mean the top source or hub of cybercriminal activity:
Russia is commonly ranked #1 in global cybercrime indices, based on expert assessments of cybercrime impact, sophistication, professionalism, and technical capability across multiple categories tied to cyber threats and organized cyber attacks.
If you mean where the most reported victim losses occur:
The United States typically reports the highest total cybercrime losses, largely because of higher reporting rates and broader coverage, not because most cybercriminals are based there. It also reflects how internal and external threats affect reporting patterns and measured loss totals.
In 2025 reporting, 22,000+ incidents were analyzed globally with 12,000+ confirmed breaches. Ransomware appeared in about 44% of breaches, while the human element contributed to about 60%. Vulnerability exploitation drove about 20% of initial access, often via edge devices and VPNs. Median dwell time was about 11 days, and criminal breakout time can be under 1 hour. Average breach cost was about $4.4M.
The top cybersecurity threat today is identity compromise, where attackers take over accounts using stolen credentials.
Key reasons:
– 97% of identity attacks involve password-spray activity.
– Phishing remains the most common entry point and drives credential theft.
– Stolen credentials are a leading factor in web app breaches and account takeovers.
Other major threats:
Vulnerability exploitation (about 33% of initial access), often via edge and VPN devices.
Ransomware/extortion (about 44% of breaches), often as the final impact after access is gained.
California ranked #1 for reported cybercrime in the U.S. based on 2024 IC3 data.
– Most complaints: 96,265 reports
– Highest losses: about $2.54B in reported victim losses
– Next highest states: Texas and Florida
These numbers reflect reported complaints and losses, so they indicate reporting volume and victim impact, not total cybercrime activity.and inconsistencies in how incidents get classified remain major potential threats to accuracy.
Kevin Mitnick is often called the world’s most famous hacker because of his high-profile cases and later work as a security consultant. He died in July 2023.
There is no single “most wanted” hacker today. Authorities pursue multiple actors at once, and some carry rewards up to $10M, such as Rim Jong Hyok, linked to state-backed and financially motivated campaigns.
Three trends dominate today: identity-led intrusion, rapid vulnerability exploitation, and ransomware tied to third-party access.
1) Identity-led intrusions
Credential theft and social engineering drive much of initial access. Phishing and vishing are rising, many intrusions are malware-free, and AI-generated phishing has increased sharply.
2) Faster vulnerability exploitation
Attackers increasingly exploit internet-facing edge and VPN systems. About 20% of breaches start here, with ~11 days median dwell time and patching lagging behind attacker speed.
3) Ransomware + third-party access
Ransomware appears in ~44% of breaches, with median payments around $115,000 and many victims refusing to pay. Third-party and supply-chain exposure has grown fast, contributing to roughly ~30% of breaches.
Get In Touch



