120 Data Breach Statistics for 2026
Data breaches have become an unavoidable part of the digital world, affecting organizations of every size with financial and personal consequences. Recent statistics highlight the scale of the issue and why it continues to demand attention.
Our analysis draws from trusted sources, including the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, Verizon DBIR 2024 and 2025, UpGuard research, ITRC findings, and Help Net Security studies. These reports highlight attack trends, financial impact, and evolving tactics, giving a solid picture of today’s risks.
So here are the 120 data breach stats for 2025.
All the sources we mentioned applies its own methodology, so numbers vary, and we include them all so readers can judge for themselves.
Data Breach Costs and Financial Impact
- The global average cost of a data breach dropped to USD 4.44 million in 2025, down from USD 4.88 million in 2024, a 9% decrease. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- In the United States, the average cost rose to USD 10.22 million, making it the most expensive region for breaches. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
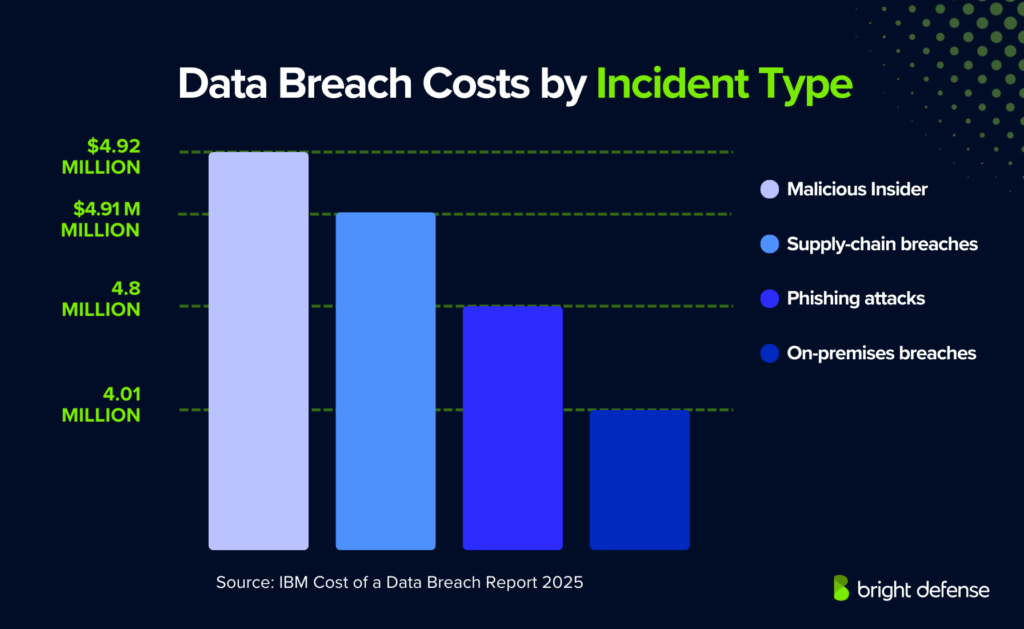
- Certain breach types proved especially expensive:
- Malicious insider attacks: USD 4.92 million.
- Supply-chain breaches: USD 4.91 million.
- Phishing attacks: USD 4.8 million.
- On-premises breaches: USD 4.01 million.
- Breaches involving multiple environments: USD 5.05 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- The type of data lost also influenced costs. Customer PII averaged USD 160 per record, while intellectual property averaged USD 178 per record. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Financial gain motivated 95% of data breaches, with the financial services industry facing some of the most damaging incidents.(Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Zero-trust reduced breach costs by USD 1.76 million (USD 4.15 million vs. 5.10 million). (Upguard)
- Cyber threats against healthcare providers also surged, raising concerns about both patient privacy and operational disruption.
- Shadow AI incidents added roughly USD 670,000 to the average breach cost, pushing the total closer to USD 4.74 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- AI played a significant role in cost differences:
- Breaches involving AI-driven attacks cost USD 4.49 million.
- Breaches tied to AI model security issues cost USD 4.46 million.
- Breaches involving shadow AI averaged USD 4.63 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- AI and automation lowered breach costs by 70%, with an average of USD 3.05 million. Detection time dropped to 249 days compared to 321 days without them. (Upguard)
- Breaches in hybrid-cloud environments averaged $3.80 million, which is $440,000 lower than private-cloud incidents. Compliance failures with major gaps added another $1.22 million to the total cost. (Upguard)
- Critical infrastructure breaches averaged USD 4.82 million, with government agencies ranking among the most frequently targeted sectors. (Upguard)
- Incident response plans reduced costs by 61%, saving USD 2.66 million. (Upguard)
- Breaches that were resolved in less than 200 days cost about USD 3.87 million, while those lasting more than 200 days climbed to USD 5.01 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- A shortage of cybersecurity skills increased breach costs sharply: organizations with high shortages paid USD 5.22 million, compared with USD 3.65 million for those with little or no shortage. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Organizations without AI or automation paid the highest average, USD 5.52 million, while those using them extensively reduced costs to USD 3.62 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Effective practices made a difference:
- Use of AI/ML insights lowered costs to USD 3.85 million compared with USD 4.9 million for low usage.
- A DevSecOps approach brought costs down to USD 3.89 million, compared with USD 5.02 million for limited adoption.
- Strong SIEM or security analytics use reduced costs to USD 3.91 million, versus USD 4.83 million when used at a low level. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Customer PII compromised through shadow AI costs slightly more than the global average, at USD 166 per record. The same pattern emerged in social engineering attacks, which frequently exploited the human element to bypass defenses. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
Phishing scams are everywhere, and they’re only getting smarter. Check out 200+ phishing stats that show just how widespread the threat really is.
AI and Automation Data Breach Impacts
- Weak safeguards played a major role in incidents. 97% of organizations that experienced AI-related breaches lacked adequate AI access controls. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- About 13% of organizations reported breaches tied directly to their AI models or applications. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Among organizations with AI governance policies:
- 45% required strict approval before use
- 39% implemented governance technology
- 36% invested in employee training
- 34% conducted scheduled audits
- 22% carried out adversarial testing (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Outcomes of AI Security Breaches. The consequences were severe:
- 60% caused a broad data compromise
- 31% triggered operational disruption (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Most AI breaches stemmed from third-party SaaS platforms (29%). Open-source and in-house models followed closely at 26% each. These third party data breaches often created ripple effects that spread beyond the original environment. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
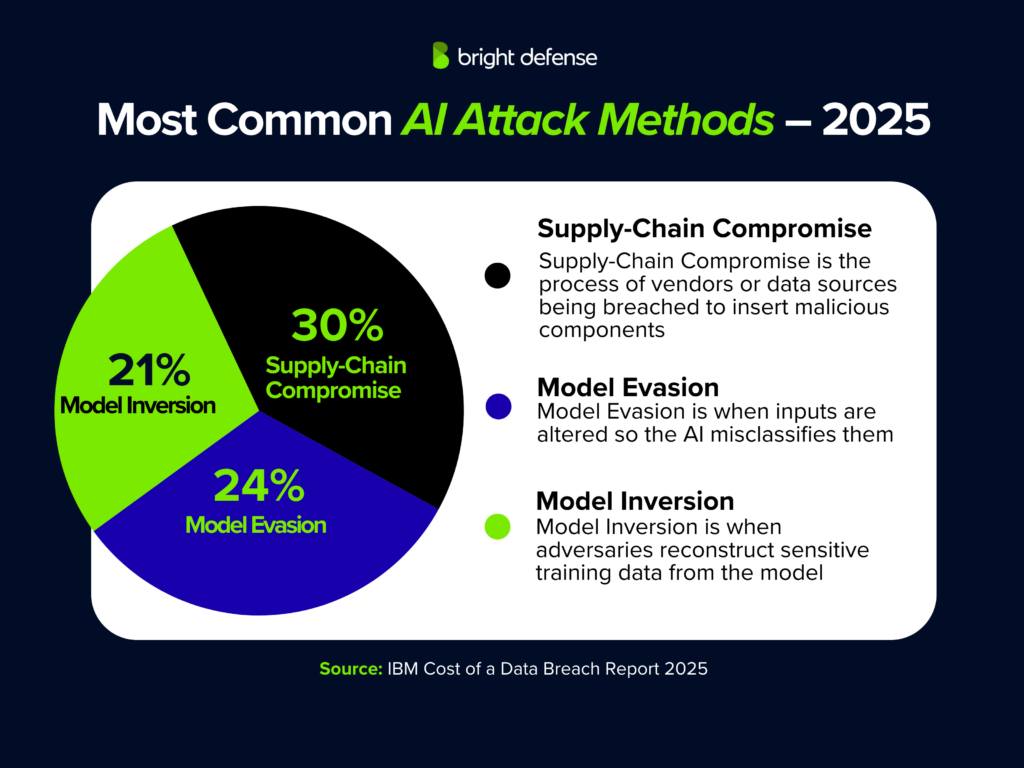
- Frequent AI data breach techniques included:
- Supply chain compromise (30%)
- Model inversion (24%)
- Model evasion (21%) (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)These attack vectors showed how easily adversaries could manipulate poorly secured systems, with insider threats occasionally compounding the damage.
- Organizations leaned on several protections against AI breaches:
- 50% relied on internal risk-assessment teams
- 38% used automated tools
- 34% hired external auditors. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Some industrial sector operators reported additional cyber incidents, citing business associate vendors as weak links in their defense posture.
- Security teams adopted AI at an impressive speed, with 77% moving as fast or faster than business units. This momentum created both opportunities and new risks that required careful oversight. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
Data Breach Detection Duration, Containment, and Resolution
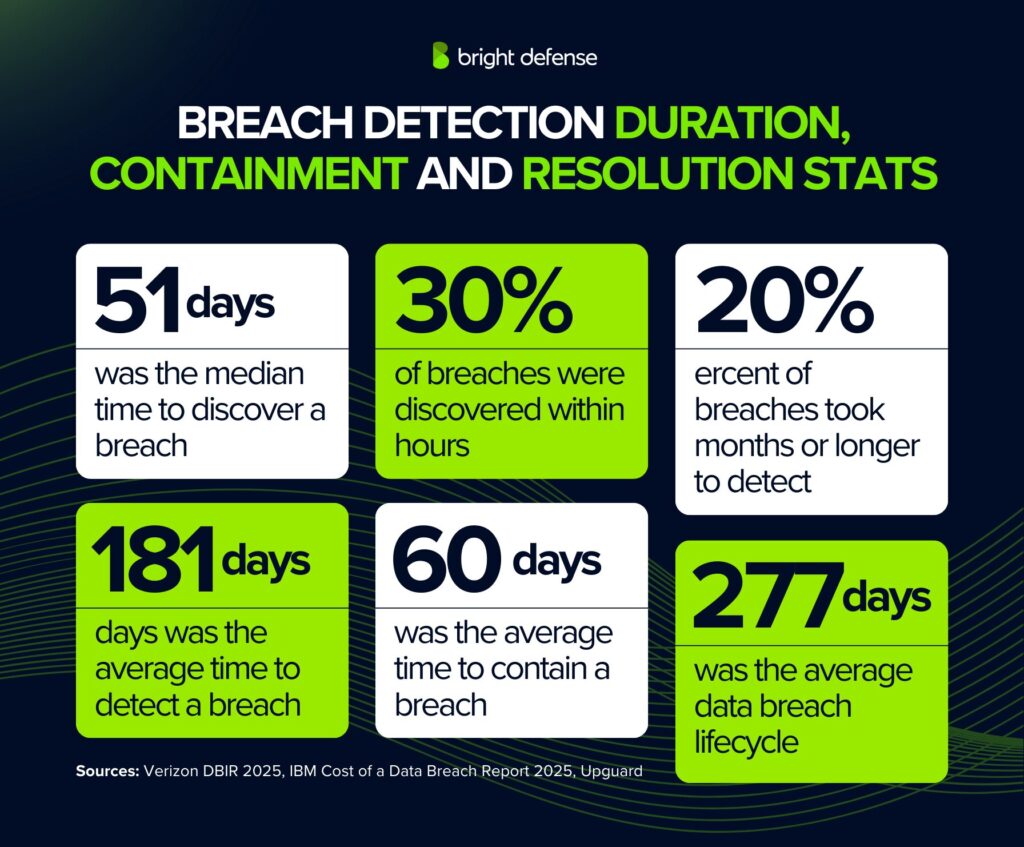
- On average, detection took 181 days and containment required another 60 days, meaning many organizations spent over eight months from breach to resolution. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- In 2024, the Verizon DBIR logged 10,626 security incidents in total. Of those, 5,176 were confirmed breaches where sensitive or customer data was exposed. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- The median discovery time for a breach was 51 days. More than 30% of breaches were found within hours, while about 20% lingered for months before being noticed. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- The average data breach lifecycle stood at 277 days. Organizations that adopted extended detection and response (XDR) technology cut this timeline down to 249 days, compared with 304 days in companies without it. (Upguard)
- By 2025, the average detection-and-containment window dropped to 241 days, the lowest in nearly a decade. Still, some categories remained slow: breaches spanning multiple environments lasted 276 days, while on-premises systems closed faster at 217 days, and public cloud cases averaged 247 days. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Attack methods showed distinct patterns. Supply-chain incidents needed 267 days, malicious insider breaches 260 days, and phishing cases 254 days. Analysts noted that these attack patterns mirrored earlier initial attack vectors like weak passwords or social engineering. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Shadow AI breaches surfaced in just 62 days but still demanded 185 days to fully contain, reflecting how AI technologies both improve detection and complicate remediation. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Use of AI and automation had a clear effect:
- Extensive use shortened detection to 51 days and containment to 153 days.
- Limited use meant 60 days to detect and 183 days to contain.
- No use meant 72 days to detect and 212 days to contain.
- Reports also showed that data breaches increased in sectors holding the most sensitive records. The financial sector accounted for a large share of incidents, but healthcare was not spared, with one dental center breach affecting thousands of patient files. Public institutions were not immune either, since multiple government entities reported attacks that exposed both citizens’ information and agency operations.
- Across all industries, millions of individuals affected suffered from fraud, account takeover, or data theft. The average total cost per breach reflected this damage, highlighting how threat actors exploit weaknesses in every environment.
Ransomware and Extortion Data Breach

- Ransomware or extortion makes up 59 to 66% of financially motivated cyberattacks. The median financial loss from these incidents is about $46,000 (Verizon)
- On average, ransom demands equaled 1.34% of a company’s revenue, with cases ranging from 0.13% up to 8.3%.(Verizon)
- One-third of breaches involved ransomware/extortion in 2024 DBIR. (Verizon)
- Ransomware accounted for 23% of incidents, while extortion alone made up 9%. (Verizon)
- Ransomware ranked as the leading threat in 92% of industries. (Verizon)
- Average ransomware breach in 2023 cost USD 4.54 million, ~8% of breaches. (Upguard)
- Ransomware breaches took ~49 days longer to detect. (Upguard)
- 28% of critical-infrastructure organizations faced destructive ransomware. (Upguard)
- Most ransomware victims refused to pay, with 63 % declining and 37 % agreeing to pay. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Fewer organizations involved law enforcement, dropping from 52 % in 2024 to 40 % in 2025. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- The average cost of a ransomware or extortion incident remained high at USD 5.08 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)

Attack Vectors and Data Breach Lifecycle
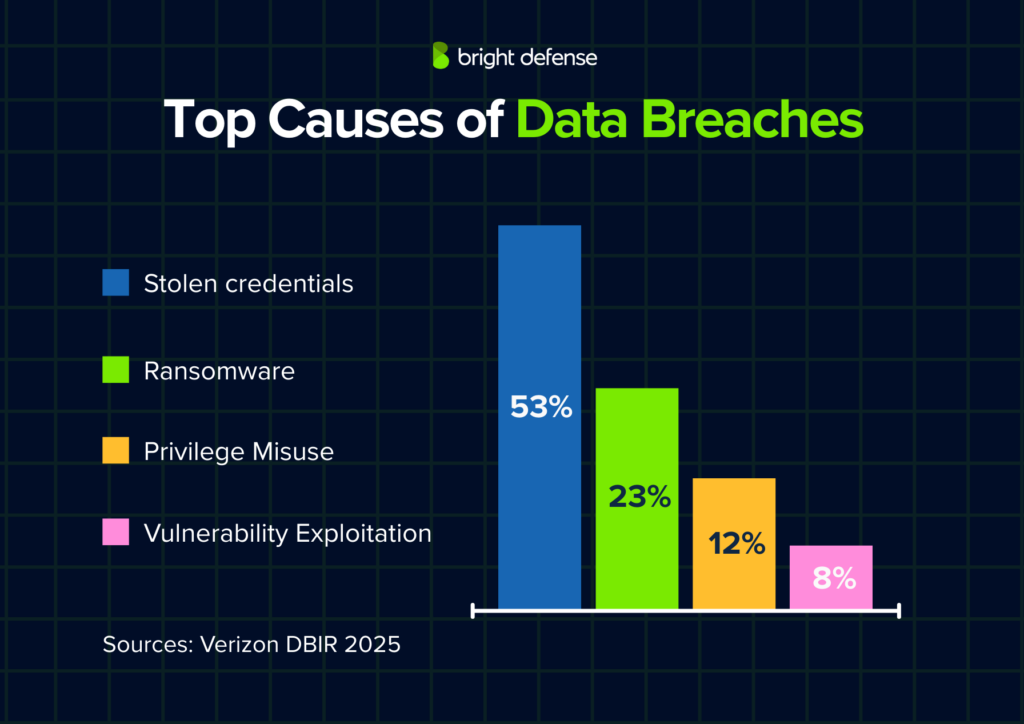
- Over half of breaches (51%) came from malicious or criminal attacks. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Stolen credentials were used in 53% of data breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Ransomware appeared in 23% of data breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Privilege misuse occurred in 12% of data breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Vulnerability exploitation appeared in 8% of data breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Physical actions occurred in fewer than 5% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- External actors caused 70% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Internal actors were responsible for 29% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- A small remaining portion involved partners or multiple actors. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Espionage accounted for 4% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Other motives represented 1% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
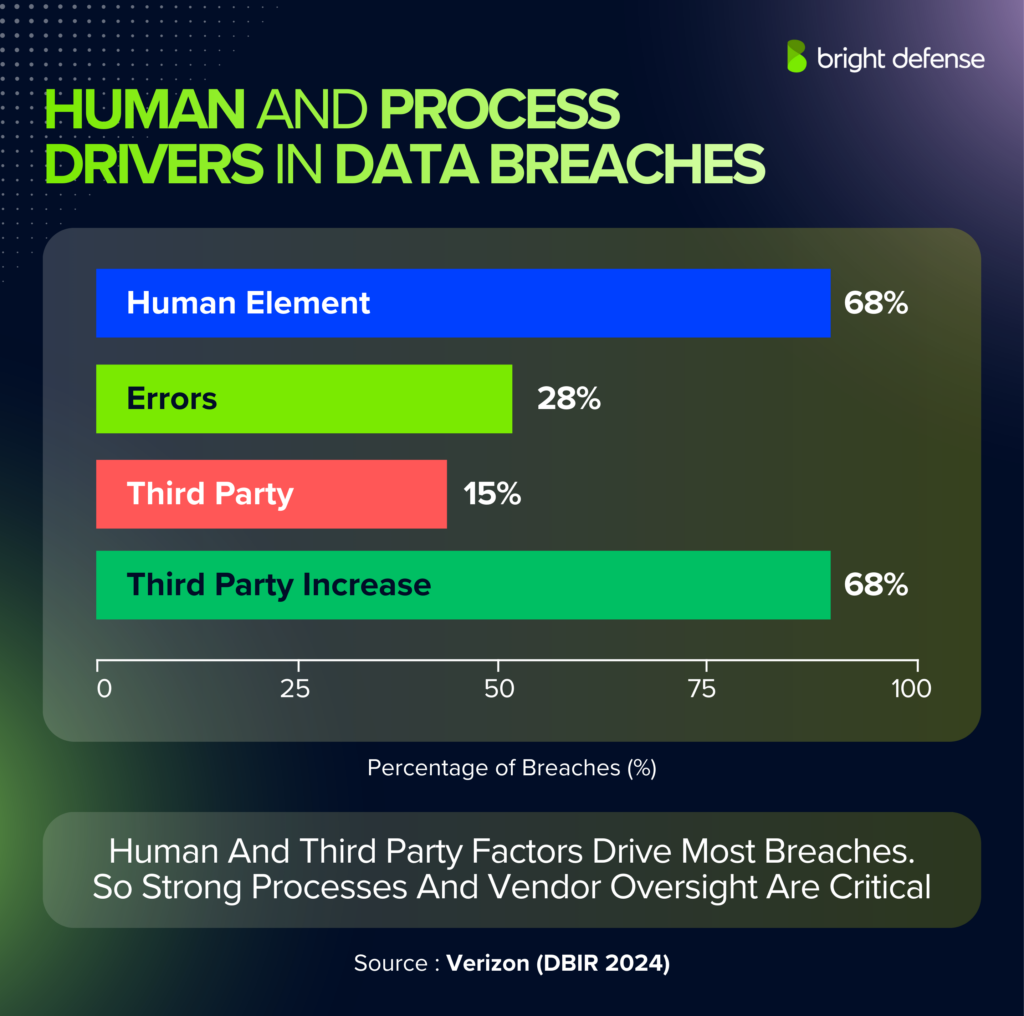
- Human error caused 26% of breaches, and IT failures accounted for 23%. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- 16% of breaches involved attackers using AI, with AI-generated phishing (37%) and deepfakes (35%) as the most common methods. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Phishing remained the most common attack vector, appearing in 16% of breaches with an average cost of USD 4.8 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Supply-chain compromise ranked as the second most common initial vector (15%) with an average cost of USD 4.91 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Exploited vulnerabilities resulted in an average cost of USD 4.24 million, while breaches caused by system errors averaged USD 3.61 million. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Credentials were compromised in 53% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Personal data was exposed in 37% of breaches, and many of these data breaches involve sensitive data that was mishandled or improperly secured. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Medical data was compromised in 13% of breaches, with several healthcare data breaches tied to ransomware campaigns that disrupted a WA healthcare provider and other regional networks. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Payment data was involved in 9% of breaches, often affecting the financial sector where cybersecurity risks remain high. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Some incidents struck global organizations, reflecting the growing trend of global data breaches that transcend national boundaries. Weak oversight of human services departments and slow adoption of security automation also played a role in prolonging recovery times. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
Human Element and Social Engineering in Data Breach

- Phishing simulations show fast victimization (21 seconds to click, 28 seconds to enter data). (Verizon)
- Social engineering appeared in 68% of breaches that involved people. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- In the accommodation and food sector, 25% of breaches involved social engineering. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Human element factored into 68% of breaches. (Verizon DBIR 2024)
- Business email compromise (pretexting) accounted for ~25% of financially motivated attacks, median loss $50,000. (Verizon)
- In phishing simulations, 20% reported suspicious messages; 11% of clickers reported afterward. (Verizon)
Did you know cybercrime costs keep climbing every year? Explore 250+ cybercrime stats that show the true scale of online threats.
Supply Chain and Third-Party Data Breach
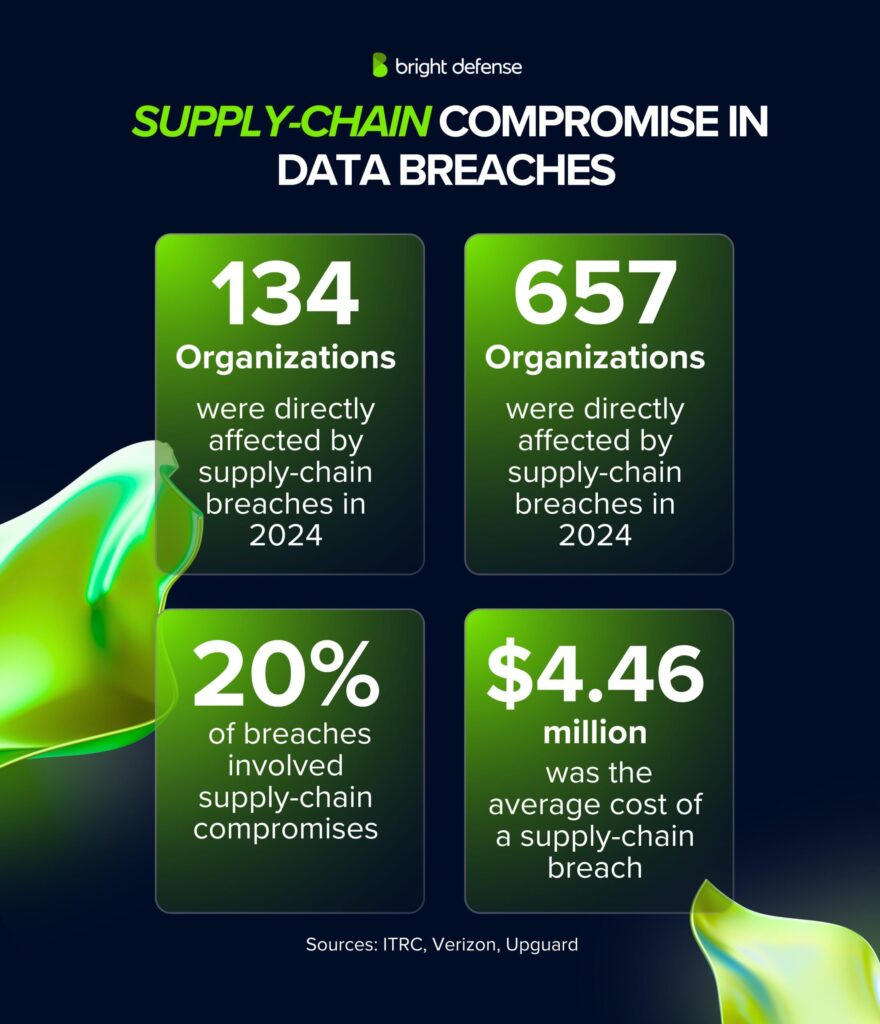
- Third-party/supply-chain breaches: 15% of incidents, up 68% due to zero-day exploits. (Verizon)
- Supply-chain breaches in 2024 directly affected 134 organizations and indirectly 657, with ~203 million notices. (ITRC)
- Supply-chain attacks in H1 2025: 79 attacks, affecting 690 organizations and 78.3 million individuals. (Help Security)
- Supply-chain compromises made up ~20% of breaches, cost USD 4.46 million on average, 26 days longer detection time. (Upguard)
- In 2024, supply chain compromises made up 15% of all incidents, which represents a 68% increase, mostly tied to zero day exploits. These cases were costly, averaging 4.46 million dollars each, and harder to spot, taking an average of 26 extra days to detect compared to other attack types.
Organizational Response and Recovery

- Only 49 % of organizations planned to increase security spending after a breach, down from 63 % a year earlier. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Just 35 % of organizations in 2025 said they had fully recovered from a breach, though this was nearly triple the 12 % in 2024. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Among those that recovered, 76 % needed more than 100 days, and 26 % needed more than 150 days. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Operational disruption was nearly universal, with 86 % of organizations affected.
- Many organizations turned to price increases after breaches:
- 45 % raised prices, down from 63 % in 2024.
- 36 % raised prices by 5–10 %, 34 % by 1–5 %, and 30 % by 15 % or more.
- Regulatory fines played a growing role: 32 % of breaches led to fines, and nearly half of those fines exceeded USD 100,000. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Fines up to USD 50,000 grew 45 %, while mid-range fines (USD 50,001–100,000) dropped by 31 %. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
Security Investment Trends

- Following breaches, less than half of organizations (49 %) planned to raise security budgets. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Top investment priorities included:
- Threat detection (43 %).
- Data protection tools (37 %).
- Incident response planning and testing (35 %).
- Among those pursuing AI-driven security:
- 45 % planned AI-powered solutions.
- Spending priorities included threat detection (36 %), incident response (35 %), data security (31 %), managed services (29 %), identity and access management (28 %), and offensive testing (28 %).
Healthcare Data Breaches
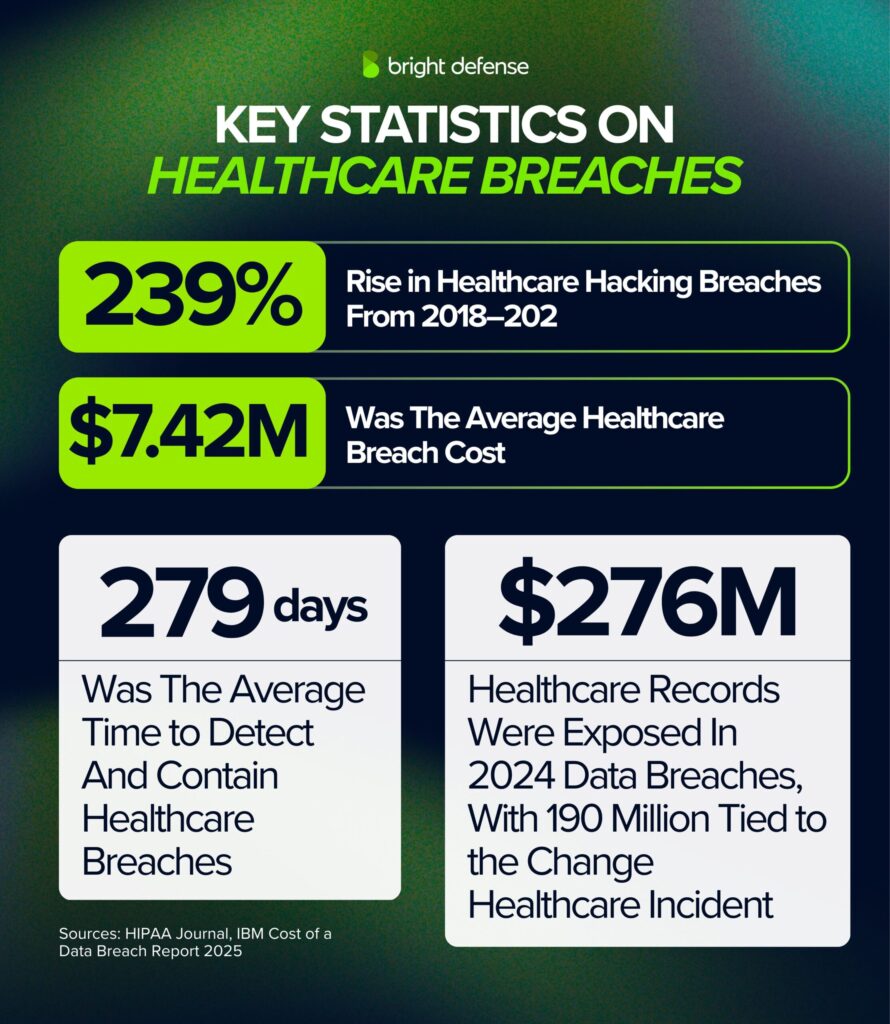
- Between 2018 and 2023, hacking-related healthcare breaches rose 239% , ransomware attacks rose 278% , and in 2023 hacking accounted for 79.7% of all breaches.. (HIPAA Journal)
- In 2023, data breaches exposed 168 million records, including 26 incidents with over 1 million records and 4 incidents with more than 8 million records. (HIPAA Journal)
- The largest healthcare breach in 2023 affected 11.27 million individuals. (HIPAA Journal)
- In 2024, data breaches exposed 276 million records, with 190 million linked to the Change Healthcare incident alone.(HIPAA Journal)
- In 2023, the healthcare sector reported 725 breaches affecting 500 or more records each, exposing a total of 133 million records. (HIPAA Journal)
- From 2009 to 2023, a total of 5,887 large healthcare breaches were reported, with 857 cases still under investigation. (HIPAA Journal)
- The healthcare sector continued to face the highest costs, with breaches averaging $7.42 million and taking 279 days to detect and contain. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Healthcare recorded the highest share of breaches caused by internal actors. (Verizon DBIR 2025)
- Within the United States, California ranks second in health care data breaches, with 22.6% of reported cases involving a CA healthcare provider.
Read Healthcare Data Breach Statistics for 2025 to Learn More About Healthcare Data Breaches.
Education and Industry-Specific Data Breach

- The accommodation and food services sector faced 220 security incidents in 2024, including 106 confirmed data breaches. Of these, 92% were caused by system intrusions, social engineering, or web application attacks. External actors were responsible for 92% of cases, while insiders accounted for 9% . (Verizon)
- The education sector experienced 1,780 security incidents in 2024, with 1,537 confirmed data disclosures. External actors were behind 68% of these cases. (Verizon)
- Personal data compromised in 83% of education breaches. (Verizon)
- Financial services recorded more breaches than healthcare, manufacturing, or tech in 2024. (ITRC)
- In the first half of 2025, the financial services sector reported 387 breaches, while the healthcare sector recorded 283. (Help Security)
Breach Volume and Victim Notices Data Breach
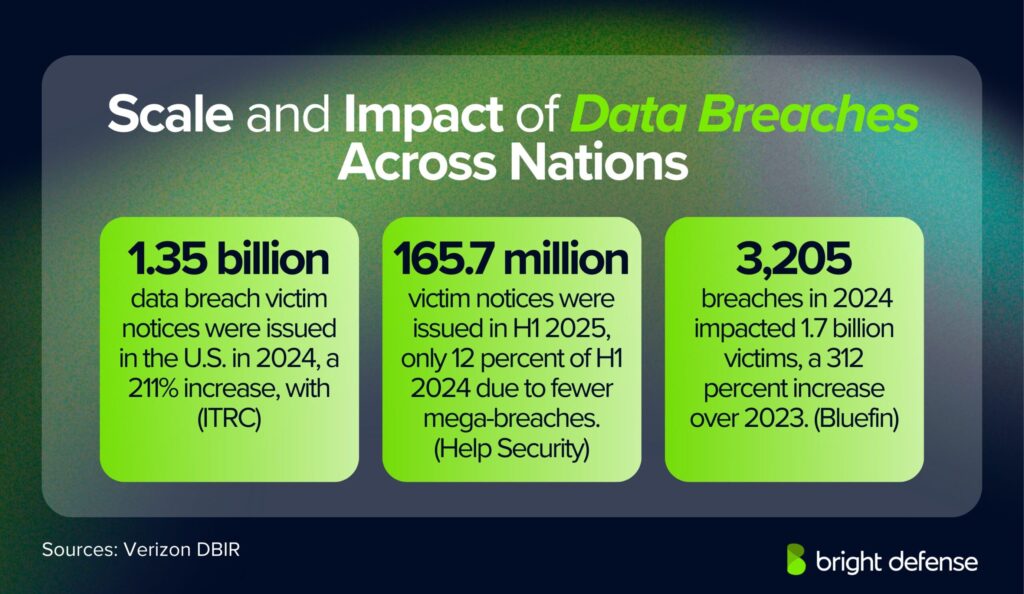
- Verizon’s 2024 DBIR recorded 30,458 security incidents worldwide, including 10,626 confirmed breaches across 94 countries. (Verizon)
- In the United States, there were 3,158 compromises in 2024, which is about 1% fewer than in 2023. (ITRC)
- U.S. victim notification letters reached 1.35 billion in 2024, a 211% jump from the prior year. Five massive breaches alone accounted for 1 billion of those notices. (ITRC)
- When those mega-breaches are excluded, 224 million notices were issued in 2024, which is 47% lower than 2023. (ITRC)
- In 2024, 70% of U.S. breach notices did not explain how the attack happened, compared to 58% the year before. (ITRC)
- Only 7% of the companies hit by mega-breaches were publicly traded, but they generated 72% of all victim notices. (ITRC)
- In the first half of 2025, 1,732 breaches were publicly reported, a 5% increase compared to the same period in 2024. (Help Security)
- Victim notices in the first half of 2025 totaled 165.7 million, just 12% of the volume seen in the first half of 2024, mainly because there were fewer mega-breaches. (Help Security)
- For mid-2025, 69% of notices did not include details on the root cause of the breach. (Help Security)
- Bluefin reported 3,205 breaches in 2024, affecting 1.7 billion victims, a 312% increase over 2023. (Bluefin)
- Breach counts rose 72% from 2022 to 2023, but victim totals that year were far lower at 353 million. (Bluefin)
- In 2024, 5,066 ransomware victim postings appeared on leak sites, a 10% increase from 2023. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- North America recorded 3,259 ransomware-related data breaches, Europe 1,136, Asia-Pacific 467, and the Middle East and Africa 184. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Manufacturing suffered 660 ransomware breaches in 2024, real estate 553, professional services 487, healthcare 443, and financial services 348. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Data breaches exposed more than 6.4 billion individual data strings. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Email entries accounted for 4.09 billion exposed records, with 2.49 billion unique addresses identified. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Phone numbers made up 3.38 billion leaked entries, with 630.9 million unique records. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Passwords represented 460 million of the leaked data points, with 161.9 million unique values. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
Shadow AI Data Breach
“Shadow AI is when employees use AI tools like ChatGPT or Midjourney without company approval. It creates risks such as data leaks, compliance violations, inaccurate outputs, and unnecessary costs, but people turn to it because these tools are fast and easy to use. Since bans rarely succeed, many companies now address shadow AI through clear policies and guardrails rather than outright restrictions.”
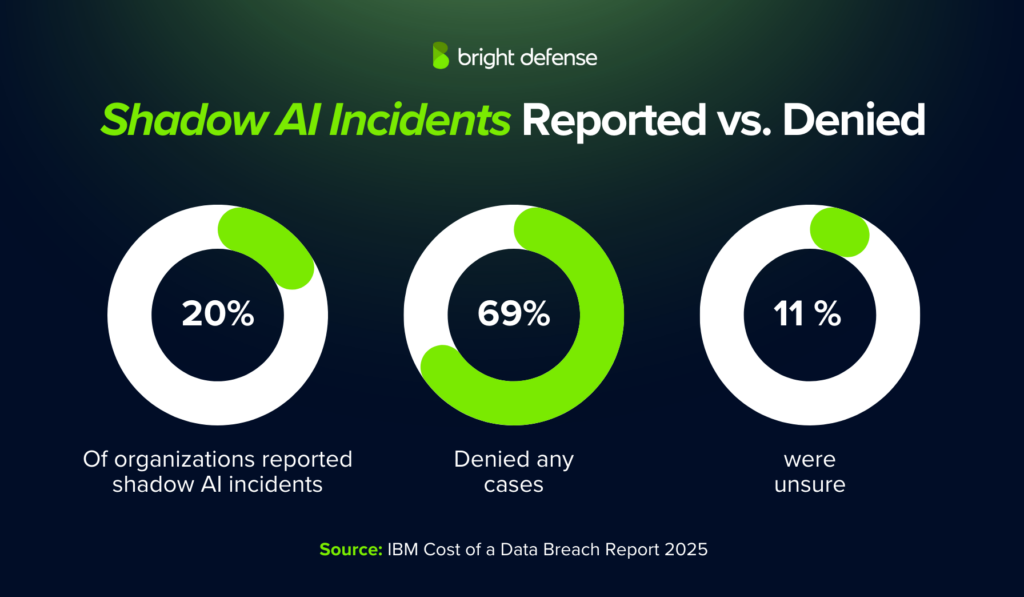
- 20 % of organizations reported shadow AI incidents, 69 % denied any cases, and 11 % were unsure. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Consequences of shadow AI incidents included:
- 44 % led to data compromise.
- 41 % increased security costs.
- 39 % disrupted operations.
- 23 % damaged reputation.
- In many cases (62 %), the compromised data was stored across multiple environments or in public cloud. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
- Data types most affected included:
- Customer PII (65 %)
- Intellectual property (40 %)
- Employee PII (34 %)
- Corporate data (31 %)
- Internal security teams detected 57 % of shadow AI incidents, while attackers disclosed only 12 %. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
Notable Global Data Breaches
- The Transport for London breach exposed bank details of around 5,000 customers and employee passwords, costing over £30 million. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- Dell Technologies reported a data breach involving 49 million customer records. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- The City of Columbus, Ohio breach compromised personal data of more than 500,000 residents after attackers claimed to steal 6.5 terabytes of data. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- A payroll breach at the UK Ministry of Defence exposed personal data of 270,000 current and former personnel. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- The Change Healthcare breach in 2024 led to an estimated $2.87 billion in financial losses and required $8.5 billion in emergency loans to healthcare providers. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- The Trello data breach exposed 15,182,079 user records, causing up to $10 million in damages. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
- The AT&T breach affected about 73 million people 7.6 million current and 65.4 million former account holders. (Reuters)
- ShinyHunters claimed the Ticketmaster breach exposed data for 560 million users through Snowflake. Treat this as an allegation rather than a confirmed final count. (SecurityWeek)
- ShinyHunters offered data for sale allegedly covering 30 million Santander customers and employees. (BleepingComputer)
- UnitedHealth said the Change Healthcare cyberattack would cost 2.3 to 2.45 billion dollars in 2024. (Forbes)
- Change Healthcare later disclosed a total of 192.7 million individuals affected. (The HIPAA Guide)
- Qantas customer data leak hit roughly 5 million Frequent Flyer records after a ransom deadline passed. (Bright Defense)
- The Synnovis attack against London hospitals led to data on an estimated 300 million patient interactions being stolen and caused more than 1,000 operations and 2,000 appointments to be canceled. (The Guardian)
- The City of Helsinki breach impacted up to 120,000 learners, guardians, and staff. (Helsinki Times)
- Advance Auto Parts reported a Snowflake-linked breach affecting more than 2.3 million people. (BleepingComputer)
- loanDepot said a January 2024 ransomware attack exposed data on 16.6 million customers. (Cybersecurity Dive)
- 23andMe agreed to a 30 million dollar settlement after a breach that exposed data for about 6.9 million customers. (Reuters)
- IT Governance tallied 44 incidents in May 2025 affecting 1,443,150,467 records. (IT Governance)
- ITRC’s 2024 report logged 3,158 compromises and said five mega breaches accounted for 83% of victim notices. (ITRC)
- AT&T reached a 177 million dollar settlement tied to its two 2024 breaches. (Statesman)
- Discord disclosed that a third-party provider breach exposed ID photos for about 70,000 users. (SecurityWeek)
- The Internet Archive breach compromised over 31 million files, including a 6.4 GB SQL database that was exfiltrated. (Group IB – Hi Tech Crime Trends)
Ransomware Data Breach Trends in 2025
United States (2025)
- 51% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 29% of encrypted cases.
- Median ransom payment: $1.5M.
- Average cost to recover: $1.91M.
- 51% fully recovered in up to a week.
Germany (2025)
- 51% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 24% of cases where data was encrypted.
- Median ransom payment: $411,600.
- Average cost to recover from a ransomware attack: $1.56M.
- 64% fully recovered in up to a week.
Japan (2025)
- 34% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 21% of encrypted cases.
- Median ransom payment: $500K.
- Average cost to recover: $0.67M.
- 50% fully recovered in up to a week.
United Arab Emirates (2025)
- 55% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 43% of encrypted cases.
- Median ransom payment: $1.33M.
- Average cost to recover: $1.41M.
- 63% fully recovered in up to a week.
Switzerland (2025)
- 53% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 10% of encrypted cases.
- Median ransom payment: $1.1M.
- Average cost to recover: $1.04M.
- 58% fully recovered in up to a week.
India (2025)
- 42% of ransomware attacks resulted in data encryption.
- Data was also stolen in 31% of encrypted cases.
- Median ransom payment: $481,636.
- Average cost to recover: $1.01M.
- 48% fully recovered in up to a week.
What Do I Do If my Social Security Number is in a Data Breach?
Quick action matters when your Social Security number is involved in a breach. Start by checking whether your information has been misused. If you see suspicious activity, report identity theft at IdentityTheft.gov or call 877-IDTHEFT. You can also request free credit reports from all three bureaus to review for new or unauthorized accounts.
Accept any free credit monitoring or identity theft insurance that the breached company offers. For added protection, place a fraud alert or credit freeze through Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion. Once you set it up with one bureau, the others receive notice automatically, reducing the chances of credential theft affecting your accounts.
The Social Security Administration recommends creating or logging into a My Social Security account to watch for benefit fraud. You should also visit the IRS Identity Theft Central page to reduce the risk of fraudulent tax returns filed in your name. Civil rights protections also extend to victims of data misuse, giving you additional avenues if sensitive information has been abused.
Finally, keep security hygiene strong. Do not carry your Social Security card in your wallet, use unique passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and stay alert to scams that involve phone or email impersonation. Employee training programs often emphasize these preventive steps, since insider threats and external actors both take advantage of poor practices.
How Do You Prepare for Data Breaches in 2025?
Based on insights from our latest data breach statistics, this guide offers a detailed, data-driven overview to help you and your organization prepare more effectively for data breaches in 2025:
1. Deploy AI-Driven Security and Automation Tools

AI and automation significantly reduced both breach costs and resolution times in 2025. Organizations without these tools paid the highest average of USD 5.52 million per breach, while those that used them extensively lowered costs to USD 3.62 million.
Automation also shortened timelines. With AI-driven detection and response, breaches averaged 249 days from identification to containment, compared to 321 days without them. In some cases, extensive automation cut detection to 51 days and containment to 153 days, versus 72 and 212 days in firms that lacked automation.
The savings were substantial:
- AI/ML insights lowered costs to USD 3.85 million, compared with USD 4.9 million for low use.
- DevSecOps integration brought costs down to USD 3.89 million, compared with USD 5.02 million in organizations with limited adoption.
- Strong use of SIEM and analytics reduced costs to USD 3.91 million, versus USD 4.83 million at low levels.
Preparation steps:
- Adopt automated detection and extended detection and response (XDR).
- Apply AI for anomaly detection and incident triage.
- Integrate automation with DevSecOps and SIEM for stronger coverage.
- Pair automation with human oversight to avoid blind spots.
2. Monitor AI and Shadow AI Usage

AI-driven risks grew sharply in 2025. 13% of organizations reported breaches tied to AI models, and 20% faced shadow AI incidents. Sensitive data often involved customer PII (65%), intellectual property (40%), and employee PII (34%).
Shadow AI proved costly, adding about USD 670,000 per breach and pushing the average to USD 4.63 million. Consequences included 44% leading to data compromise, 41% higher security costs, and 39% operational disruption.
Weak governance was a clear factor: 97% of AI-related breaches lacked proper access controls. Attackers exploited supply chain compromise (30%), model inversion (24%), and model evasion (21%).
Where governance existed, protections included strict approval policies (45%), audits (34%), and adversarial testing (22%), all of which reduced exposure.
Preparation steps:
- Maintain an inventory of all AI tools.
- Enforce approvals and access controls.
- Audit regularly and conduct adversarial tests.
- Monitor SaaS AI platforms closely, since they caused 29% of AI breaches.
3. Prepare for Ransomware with Backups and Refusal Strategies

Ransomware remains one of the most damaging attack types in 2025. It accounted for 23% of data breaches and, together with extortion, made up 59–66% of financially motivated cyberattacks. The average cost per incident reached USD 5.08 million, higher than many other breach categories.
Victims faced tough decisions. 63% refused to pay ransoms, while 37% agreed. Ransom demands typically equaled 1.34% of company revenue, with some cases reaching 8.3%. Adding to the challenge, ransomware breaches took about 49 days longer to detect than other incidents.
Critical sectors were hit hard: 28% of critical infrastructure organizations reported destructive ransomware attacks, while healthcare and financial services saw prolonged disruptions.
Preparation steps:
- Maintain offline, encrypted backups and test them frequently.
- Define clear ransom payment or refusal policies before an attack occurs.
- Rehearse ransomware scenarios in incident response exercises.
- Involve law enforcement where possible, despite reports showing only 40% of victims engaged authorities in 2025 (down from 52% in 2024).
4. Apply Consistent Controls Across Environments
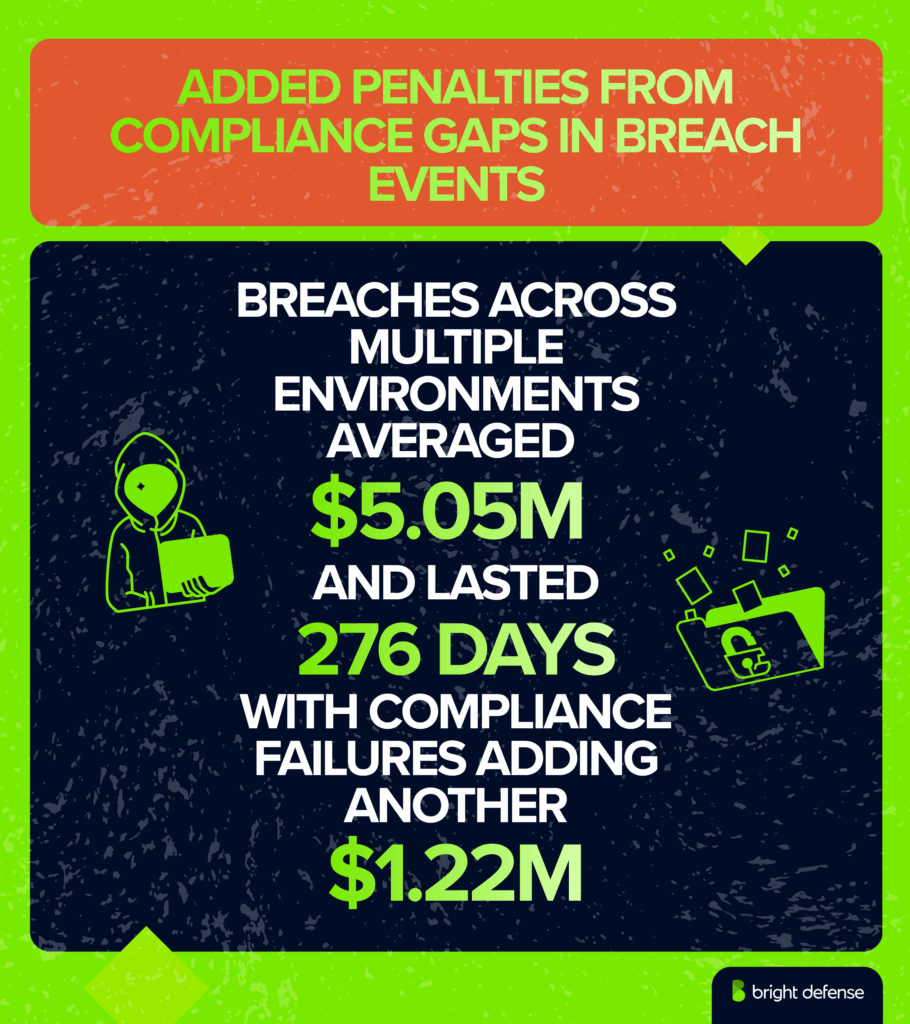
Breaches spanning multiple environments proved especially costly in 2025, averaging USD 5.05 million compared with USD 4.01 million for on-premises cases and USD 3.80 million for hybrid cloud. Multi-environment incidents also lasted longer, with an average lifecycle of 276 days, compared with 217 days for on-premises and 247 days in public cloud.
Compliance failures compounded the problem, adding about USD 1.22 million to total breach costs. Inconsistent security policies across hybrid, private, and public cloud often created exploitable gaps, giving attackers opportunities to move laterally.
Preparation steps:
- Enforce uniform access controls, encryption, and monitoring across all environments.
- Apply zero-trust principles consistently to limit lateral movement.
- Centralize visibility through SIEM or XDR to avoid blind spots.
- Regularly review compliance obligations to prevent costly fines and penalties.
Did you know most companies struggle with cybersecurity compliance? Explore 150 compliance stats that reveal the biggest challenges and trends.
5. Invest in Employee Awareness

Human factors remain the single largest driver of breaches. In 2025, 68% of incidents involved the human element, and phishing alone accounted for 16% of breaches, with an average cost of USD 4.8 million. Verizon simulations showed users clicked within 21 seconds of receiving a phishing email, and data was entered within 28 seconds.
Business email compromise also grew, making up about 25% of financially motivated attacks, with a median loss of USD 50,000.
Preparation steps:
- Deliver ongoing phishing and social engineering training, not just annual refreshers.
- Reinforce safe handling of PII and intellectual property.
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reduce the impact of stolen credentials.
- Track employee reporting rates during phishing simulations to measure progress.
6. Rehearse Incident Response

Testing incident response plans continues to pay off. Organizations that had a rehearsed plan reduced breach costs by 61%, saving around USD 2.66 million. Breaches resolved in under 200 days averaged USD 3.87 million, compared with USD 5.01 million when containment dragged past that point.
Still, many organizations lag in preparedness. In 2025, only 35% said they had fully recovered from a breach, though that was an improvement from 12% in 2024. Recovery often took over 100 days, and in a quarter of cases more than 150 days.
Preparation steps:
- Conduct tabletop and live-fire exercises for ransomware, AI-driven, and supply-chain attack scenarios.
- Involve executive leadership, legal teams, and technical staff to test decision-making.
- Measure containment times after drills and refine procedures to accelerate response.
- Integrate lessons learned into updated playbooks.
7. Strengthen Vendor and Supply-Chain Security
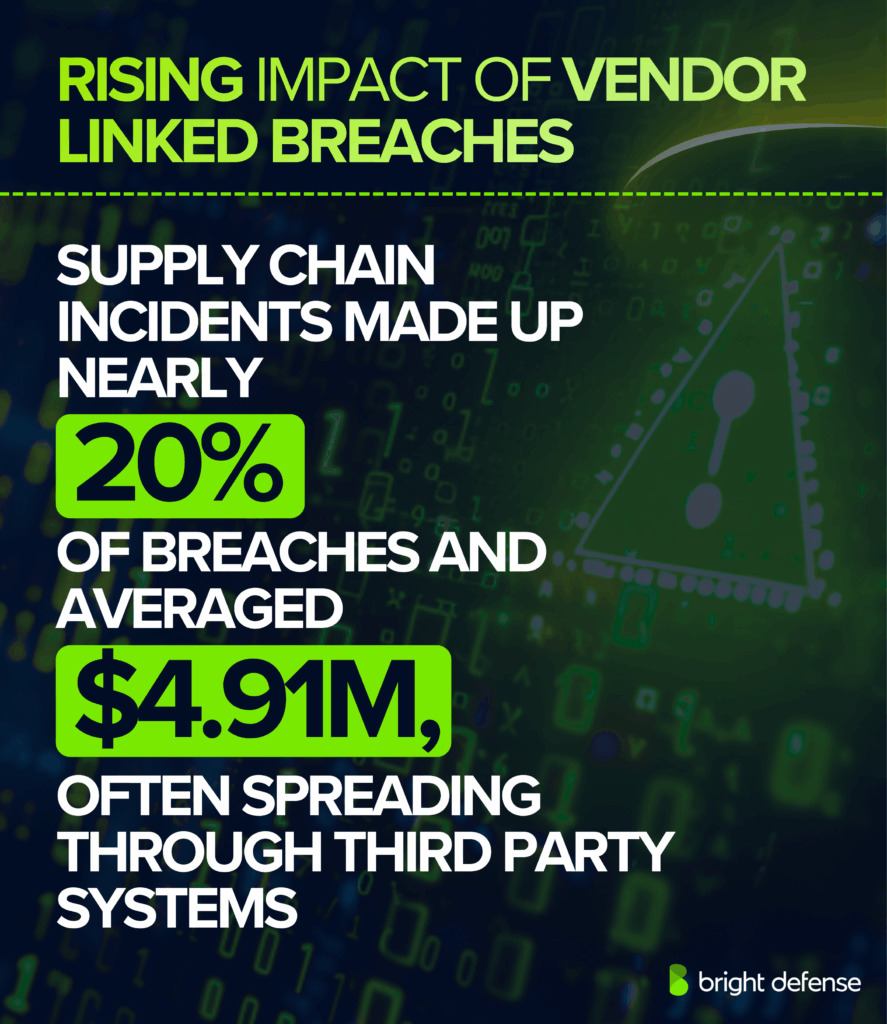
Supply-chain breaches surged in 2025 and became one of the most disruptive attack vectors. They accounted for nearly 20% of all breaches, up sharply from 15% the year before. These incidents averaged USD 4.91 million in costs and took about 26 days longer to detect compared with other types.
The ripple effects were significant. In the first half of 2025 alone, 79 supply-chain attacks impacted 690 organizations and 78.3 million individuals. Many originated from third-party SaaS or vendor systems with weaker defenses. The 2024 ITRC report also recorded cases where a single compromise directly affected 134 organizations and indirectly spread to more than 650 others.
Preparation steps:
- Require vendors to provide regular security attestations and proof of patching.
- Limit data sharing with suppliers to the absolute minimum.
- Monitor third-party connections continuously for unusual activity.
- Build contractual obligations around incident notification and response times.
- Include supply-chain breach scenarios in incident response rehearsals.
Trends shaping the 2025 breach environment
- Breach costs remain high: Global average fell 9% to USD 4.44M, but U.S. breaches still average USD 10.22M. Healthcare (USD 7.42M) and finance rank highest.
- AI drives both sides: 16% of breaches used AI attacks (phishing, deepfakes). Organizations with full AI and automation cut costs to USD 3.05M and detect incidents in 249 days. Zero-trust adoption saves another USD 1.76M.
- Vendor and supply-chain risk grows: Nearly 30% of breaches stemmed from supply chains, averaging USD 4.91M each. Oversight gaps leave many firms exposed.
- Ransomware and extortion persist: Ransomware in 44% of breaches. Median payments dropped to USD 115K. SMBs hit hardest (88% of their breaches), while 64% of victims overall refused to pay.
- Credentials and human error dominate: Stolen credentials (22%), vulnerabilities (20%), phishing (15–16%). Human error in 60% of breaches keeps awareness vital.
- Attack patterns shift: System intrusion leads at 53%, followed by social engineering (17%) and web app attacks (12%). Exploited flaws up 34%, stressing patch urgency.
- AI governance becomes critical: Nearly all AI-related breaches lacked access controls. 63% had no AI policy. Shadow AI drove 20% of cases, often exposing sensitive data.
How Bright Defense Can Help
Bright Defense helps organizations cut down the conditions that lead to data breaches. Our team strengthens controls across cloud and on-prem systems, runs targeted penetration testing to expose entry points attackers often use, and supports security training that reduces phishing and other user-driven risks.
We also provide vCISO guidance and incident support that keeps response efforts organized and limits the impact when an incident occurs.
These combined services create stronger visibility, faster detection, and tighter protection around sensitive data. Bright Defense can help your organization lower breach likelihood and improve readiness when threats emerge.
FAQs
The latest verified U.S. annual benchmark from the Identity Theft Resource Center shows a record 3,322 data compromises in 2025, which the report describes as a 79% increase over five years. The same report also says total victim notices fell from 1.36 billion in 2024 to 278.8 million in 2025.
Verizon’s 2025 DBIR says ransomware remained a major issue and was present in 44% of reviewed breaches, up from 32%, with a 37% increase from the prior report year. Verizon also notes a median ransom payment of $115,000 and says 64% of victim organizations did not pay.
Recent Verizon reporting shows credential abuse and vulnerability exploitation are leading initial access paths, with an official summary highlighting credential abuse (22%), exploitation of vulnerabilities (20%), and phishing (16%) among known initial access vectors in the analyzed breach set. Verizon also reports edge device and VPN exploitation activity at 22% of vulnerability exploitation actions and a median 32 days to full remediation for those edge device issues.
IBM reports a $4.4 million global average cost of a data breach in its 2025 report, a 9% decrease from the prior year, and links that drop to faster identification and containment. The same IBM page also reports 97% of organizations with an AI-related security incident lacked proper AI access controls and 63% lacked AI governance policies.
No. ITRC survey findings in its 2025 report show 88% of respondents who received a breach notice experienced at least one negative consequence, and only 9.7% reported ignoring the notice or doing nothing.
The first steps should be immediate account protection and fraud monitoring, and FTC guidance directs people to use IdentityTheft.gov/databreach, report identity theft at IdentityTheft.gov, and report fraud at ReportFraud.ftc.gov. FTC consumer guidance also recommends steps such as changing passwords and placing a fraud alert or credit freeze when personal information is exposed.
No. Credit monitoring can help detect some misuse, but it does not stop all fraud types, account takeover attempts, or phishing that often follows a breach notice. ITRC reports that 54% of consumers saw more targeted phishing attempts after a breach, and many people took added actions such as changing passwords and setting up passkeys.
The strongest 2026 prediction is that AI will shape both attacks and defense, while fraud, phishing, and supply-chain risk stay major concerns. The World Economic Forum reports 94% of leaders expect AI to be the most consequential force in cybersecurity in 2026, 87% saw rising AI-related vulnerabilities, 73% said they were or knew someone affected by cyber-enabled fraud in 2025, and 65% of large companies cited third-party and supply-chain risk as their biggest cyber resilience barrier.
A few current benchmark statistics are: Verizon’s 2025 DBIR reviewed 22,052 security incidents and 12,195 confirmed data breaches, found ransomware in 44% of breaches (up from 32%), and reported the human element in about 60% of breaches, while third-party involvement rose from 15% to 30%. IBM’s 2025 report lists a $4.4M global average data breach cost and says 97% of organizations with an AI-related security incident lacked proper AI access controls.
There is no single official global total for 2025. For a strong U.S. public-report benchmark, the Identity Theft Resource Center recorded 3,322 data compromises in 2025, up from 3,152 in 2024 (about 5%), while victim notices fell 79% to about 278.8 million. Separately, Verizon’s 2025 DBIR dataset included 12,195 confirmed data breaches, but that is a research dataset count, not a full global total.
Get In Touch



