SOC 2 Penetration Testing Requirements in 2025
Achieving SOC 2 compliance in 2025 has shifted from a nice-to-have to a baseline requirement for technology companies. Auditors now demand proof that security controls function under real conditions, not just exist in policy documents. This article explains what SOC 2 expects from penetration testing in 2025.
If you are managing security or compliance, you are probably asking whether your current penetration testing approach meets today’s stricter demands. Many teams run into trouble because of outdated reports, poor scoping, or missing retest evidence. These gaps delay audit results, hurt client trust, and put revenue tied to security reviews at risk.
Mistakes often include relying on automated scans without human validation or scheduling tests outside the audit window, both of which auditors now reject.
This article gives you clear, direct guidance to meet SOC 2 penetration testing requirements in 2025 and avoid costly missteps.
Is Penetration Testing a Requirement for SOC 2?
No, penetration testing is not a formal requirement to achieve SOC 2 compliance. SOC 2 reports are based on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC), which focus on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. The standard does not mandate a specific list of technical assessments, including penetration tests, for compliance.

SOC 2 primarily evaluates whether an organization has controls in place and whether those controls are effective over time. Penetration testing can contribute valuable evidence but remains an optional method within the broader framework of control evaluation.
How Does Penetration Testing Support SOC 2?
While penetration testing is not compulsory, auditors often view it as a practical tool to support specific components of the Trust Services Criteria (TSC), particularly under the domain of Monitoring Activities.
Key references include:
- COSO Principle 16:
“The entity selects, develops, and performs ongoing and/or separate evaluations to ascertain whether the components of internal control are present and functioning.” (Linford) .
- TSC Common Criteria (CC) 4.1 — Point of Focus:
“Management uses a variety of different types of ongoing and separate evaluations, including penetration testing, independent certifications made against established specifications (for example, ISO certifications), and internal audit assessments.” (Linford)
These references do not mandate penetration testing but mention it as one of several methods organizations can use to satisfy evaluation expectations.
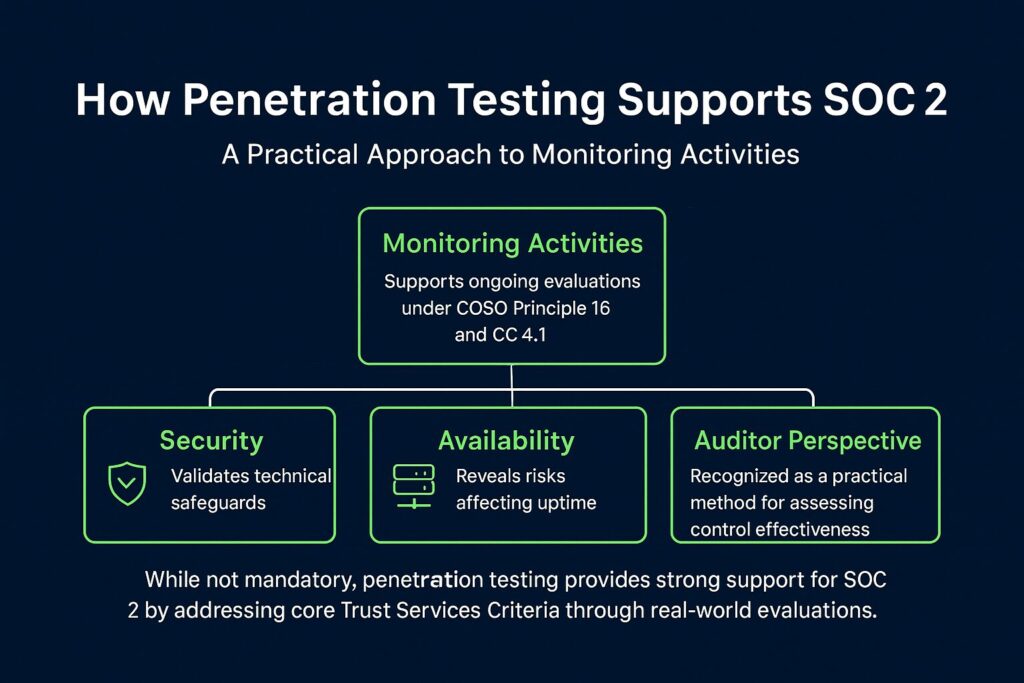
The guidance allows different evaluation approaches based on risk tolerance and operational needs, encouraging methods that can identify potential vulnerabilities effectively.
Penetration testing also supports several key Trust Services Principles and related criteria:
- Security Principle — CC4.1 (Validating Security Controls)
“The entity selects, develops, and performs ongoing and/or separate evaluations to ascertain whether the components of internal control are present and functioning.”
Penetration testing provides an active check on controls beyond policy reviews. It attempts real-world exploitation of vulnerabilities, measuring the effectiveness of technical safeguards like firewalls, endpoint protections, and access restrictions. This validation directly supports the Security principle across organization’s systems.
- Availability Principle — A1.2 (Identifying Unknown Weaknesses)
“The entity authorizes, designs, develops, or acquires, implements, operates, approves, maintains, and monitors environmental protections, software, data backup processes, and recovery infrastructure to meet its objectives.”
Penetration testers use tactics that uncover risks traditional scanning often misses. These risks, if exploited, could affect system uptime. Strengthening defenses based on penetration test results helps meet the Availability principle by safeguarding critical systems and infrastructure.
- Confidentiality Principle — C1.1 (Assessing Data Breach Risk)
“The entity identifies and maintains confidential information to meet the entity’s objectives related to confidentiality.”
Through simulated attacks on sensitive data, penetration testing helps organizations understand how an attacker might compromise confidential information. This provides a clearer picture of data protection measures and supports compliance with the Confidentiality principle.
In short, while SOC 2 does not explicitly require penetration testing, auditors recognize it as a strong, practical method for validating an organization’s security posture. It not only satisfies expectations under Monitoring Activities but also addresses security, availability, and confidentiality requirements through specific TSC principles.
How Much Does SOC 2 Penetration Testing Cost?
The cost of SOC 2 penetration testing depends on scope, system complexity, and provider expertise. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how much SOC 2 penetration testing services may cost you:

- Basic Tests: $5,000–$10,000
Focus on meeting compliance requirements with limited depth and supporting system availability needs. - Comprehensive Tests: $15,000–$30,000
Deliver deeper analysis, including vulnerability assessments and detailed recommendations, often addressing separate risk factors across environments. - Specialized Testing: $50,000+
Suited for large or complex infrastructures that require network security evaluations, remediate identified deficiencies, and protection against cyber threats.
At Bright Defense, we offer exclusive discounts for our readers. If you are preparing for SOC 2 and need penetration testing services, reach out to us, mention this article, and we’ll extend a special discount on your next SOC 2 penetration test.
What is the Duration for SOC 2 Penetration Testing?
SOC 2 penetration testing usually takes 2 to 6 weeks. Smaller environments with limited systems may take around 2 to 3 weeks, while larger or more complex environments with multiple applications and networks can extend closer to 6 weeks.
The timeline includes scoping, testing, reporting, and time for any necessary clarifications such as addressing newly discovered vulnerabilities or performing control testing as part of the process. Organizations with intricate setups might also require continuous monitoring to maintain readiness during extended assessments.
What Happens If You Fail to Meet SOC 2?
Failing to achieve SOC 2 compliance can have serious consequences, especially for organizations that handle customer data or provide cloud-based services. The effects touch on business reputation, security objectives, customer trust, and legal exposure.
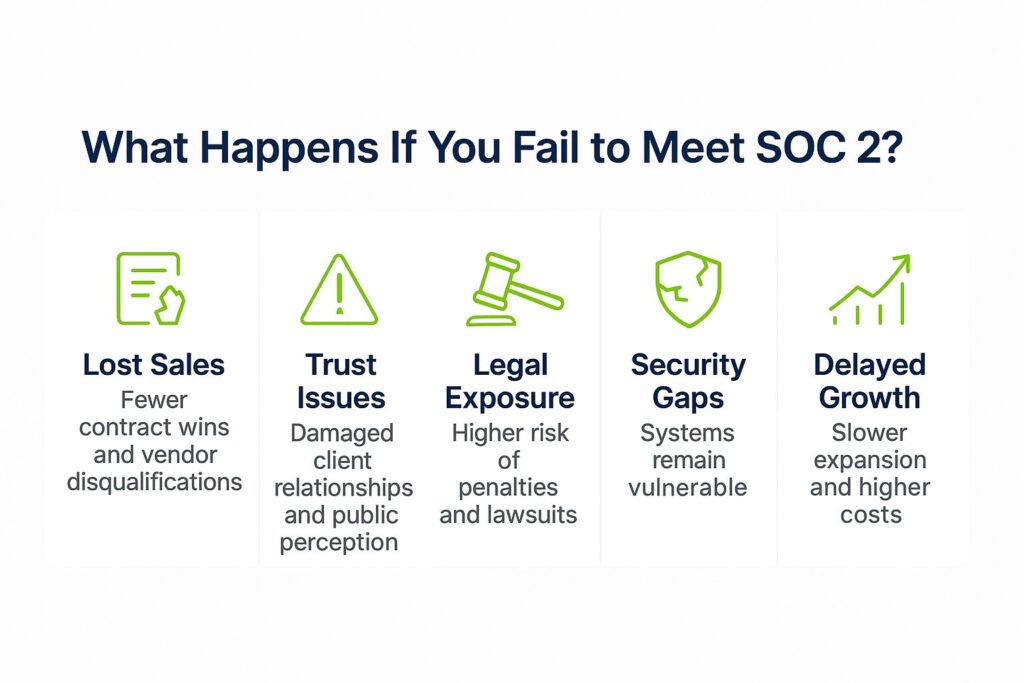
The following are some of the issues you may face:
- Lost Sales: Disqualification from vendor lists and fewer contract wins as potential clients opt for competitors who meet security measures expectations, often evaluating companies based on their security practices.
- Trust Issues: Clients may doubt the company’s ability to protect customer data, which can lead to damaged relationships and public perception problems. Strengthening vulnerability management efforts can help address these concerns.
- Legal Exposure: Higher risk of penalties and lawsuits after breaches, since lack of compliance often signals inadequate risk management and controls, exposing the company to potential security threats.
- Security Gaps: Critical weaknesses in controls and processes remain unaddressed, leaving the organization vulnerable to internal failures and external threats.
- Delayed Growth: Extended remediation timelines slow down business expansion plans, causing missed opportunities and higher costs for corrective actions.
Do You Need Vulnerability for Scanning SOC 2 Compliance?
No, vulnerability scanning is not a strict requirement for SOC 2 compliance. However, it supports meeting the Security Trust Services Criteria, especially under:
- CC3.1 (Control Environment): Requires organizations to show a commitment to security and risk management practices.
- CC5.2 (Control Activities): Requires monitoring of system changes and risk exposures, where regular scanning can serve as evidence.
- CC7.1 (System Operations): Focuses on detecting and monitoring security events — vulnerability scans help identify and respond to weaknesses proactively.
- CC7.2 (Change Management): Scanning tools help monitor for unapproved or risky system changes.
- CC7.3 (Risk Mitigation): Involves assessing and addressing vulnerabilities, where scanning plays a key role.
While not explicitly required, vulnerability scanning demonstrates a proactive security approach, strengthening your SOC 2 audit posture.
Benefits of Having Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scanning for SOC 2
Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning are not mandatory for SOC 2, but they offer significant advantages. These practices show auditors that your security program is active and effective, helping you meet key Trust Services Criteria and maintain data security.
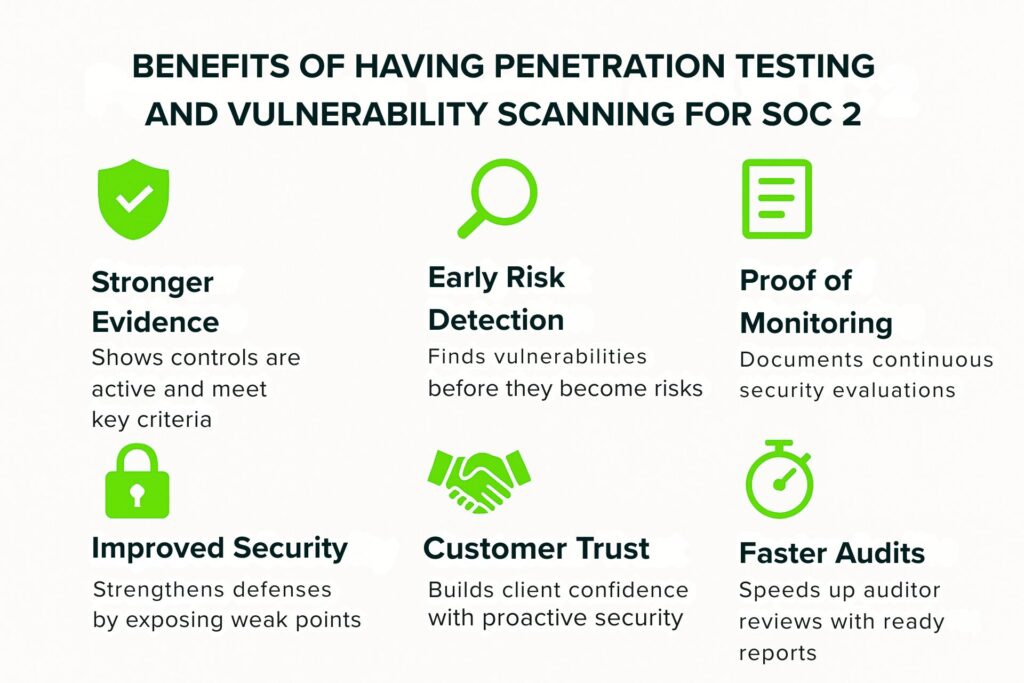
- Stronger Evidence for Auditors: Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning show that your controls are active and effective, supporting the Security, Availability, and Confidentiality criteria while strengthening internal control practices.
- Early Risk Detection: Regular scans and tests catch vulnerabilities before they turn into real risks, reducing the chance of audit findings or breaches. They also help detect potential vulnerabilities early in the process.
- Proof of Continuous Monitoring: SOC 2 requires ongoing evaluation of system security (CC7.1, CC7.2). These activities provide documented proof of continuous monitoring efforts.
- Improved Security Posture: Testing and scanning expose weak points that can be fixed early, improving overall defense against attacks.
- Customer and Partner Trust: Demonstrating proactive security efforts helps build confidence with clients who expect strong protection of their data.
- Faster Audit Process: Having testing and scanning reports ready speeds up auditor reviews and reduces back-and-forth during the audit.
Difference Between a SOC 2 Pentest and Regular Penetration Testing
There isn’t much difference between a regular pen test and a SOC 2 pentest, except that SOC 2 pentests are done with the intention to meet SOC 2 compliance.
| General Penetration Test | SOC 2 Pentest | |
| Purpose | Find security weaknesses | Provide evidence for SOC 2 controls |
| Scope | Company defines it | Matches SOC 2 in-scope systems |
| Audience | Security and IT teams | Auditors and compliance teams |
| Documentation | Standard report | Audit-ready report with remediation |
| Timing | Flexible | Must fit audit period |
| Requirement | Based on security goals | Not required but often recommended |
1. Penetration Testing (General)
Penetration testing is a security assessment where testers try to exploit vulnerabilities in systems, applications, or networks. It checks how attackers could gain unauthorized access or disrupt services.
- Focuses on finding and fixing technical weaknesses using a structured testing methodology.
- Scope is based on the company’s decision (e.g., external network, web app) and often includes setting strict access controls to limit potential exposure.
- Results in a report listing vulnerabilities and recommendations based on adequate security measures to prevent future risks.
- Timing is flexible — done annually, after major changes, or when needed.
Penetration tests serve security improvement goals. They are not linked to any specific audit unless requested.
2. SOC 2 Pentest
A SOC 2 pentest is not a separate type of test. It is a penetration test performed to support SOC 2 audits. It provides evidence that appropriate controls and security measures are working.
- Focus is on the systems included in the SOC 2 audit and evaluates system availability as part of the overall assurance.
- Supports the Trust Services Criteria (especially Monitoring Activities like CC4.1) through consistent monitoring procedures.
- The test needs clear documentation and proof of remediation.
- It must fall within the audit review period, especially for SOC 2 Type II.
A SOC 2 pentest is the same technical exercise but tailored to meet audit needs.
Bright Defense Offers Penetration Testing for SOC 2 Compliance
At Bright Defense, we offer penetration testing services designed to meet the strict requirements of SOC 2 compliance. Whether you’re preparing for your first audit or maintaining an ongoing attestation, our testing process uncovers vulnerabilities and new vulnerabilities that auditors expect organizations to address.
We deliver focused assessments on applications, networks, and APIs, simulating real-world attack scenarios that test your controls against industry standards. Our process not only highlights technical gaps but also provides actionable reports mapped directly to SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria, supporting your audit evidence with clarity and precision through a compliance assessment.
Bright Defense’s team brings deep expertise in security compliance, having helped businesses across industries achieve and maintain compliance with SOC 2 certification. With cutting-edge tools, proven methodologies, and experience across cloud and hybrid environments, we help organizations reduce audit friction and strengthen their security posture.
Working with Bright Defense, you position your organization to meet SOC 2 requirements confidently while building greater trust with customers and partners.
Learn more about our approach to secure your compliance journey: brightdefense.com
FAQ
Does SOC 2 require penetration testing?
No, SOC 2 does not mandate penetration testing, but it is highly recommended to show the effectiveness of security controls through comprehensive penetration testing where necessary.
Is vulnerability scanning a requirement for SOC 2?
No, but regular vulnerability scanning supports the Security Trust Services Criteria and strengthens audit readiness, especially when paired with data classification practices.
Should I perform a pentest as part of my SOC 2 audit?
Yes, a penetration test helps demonstrate that security controls are effective, reducing security risks and making it valuable for a smoother audit.
What is SOC 2 penetration testing?
Testing that simulates real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls for systems within the SOC 2 audit scope.
What is a SOC 2 test?
An evaluation of a company’s controls against the SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria, focusing on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
What is the difference between penetration testing and SOC?
Penetration testing checks for security weaknesses through simulated attacks. SOC (System and Organization Controls) reports assess organizational controls based on predefined criteria, like SOC 2 for data protection.
What are the three types of penetration tests?
- Black-box testing: No prior knowledge of the system.
- White-box testing: Full knowledge of the system.
- Gray-box testing: Partial knowledge of the system.
Get In Touch