
SOC 2 Type II – Who Needs This Report and Why It Matters
The financial impact of data security failures has reached unprecedented levels, with IBM reporting that the average cost of a data breach hit $4.44 million in 2025, marking a 15% increase over three years.
Gartner Digital Markets reported that almost half (46%) of the software buyers chose a vendor because of security certification, reputation, or data privacy practices.
At a time where a single security incident can derail partnerships and damage reputation, organizations like yours need verifiable evidence of your commitment to protecting sensitive information.
A SOC 2 Type 2 report is exactly that kind of proof. It is an independent audit report that shows how your security controls hold up over time. Many B2B and SaaS companies now treat it as a must have because customers want to see real evidence, not promises.
This guide breaks down the basics of SOC 2 Type 2 compliance, shows how it compares to other security frameworks, explains the real business benefits, and walks through the steps to earn the certification.
What is a SOC 2 Type II Report?
SOC 2 Type II is an independent audit report that assesses how effectively a company’s data security controls operate over a defined period of time. An outside auditor reviews the organization’s controls against the AICPA Trust Services Criteria, including security and, when applicable, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.

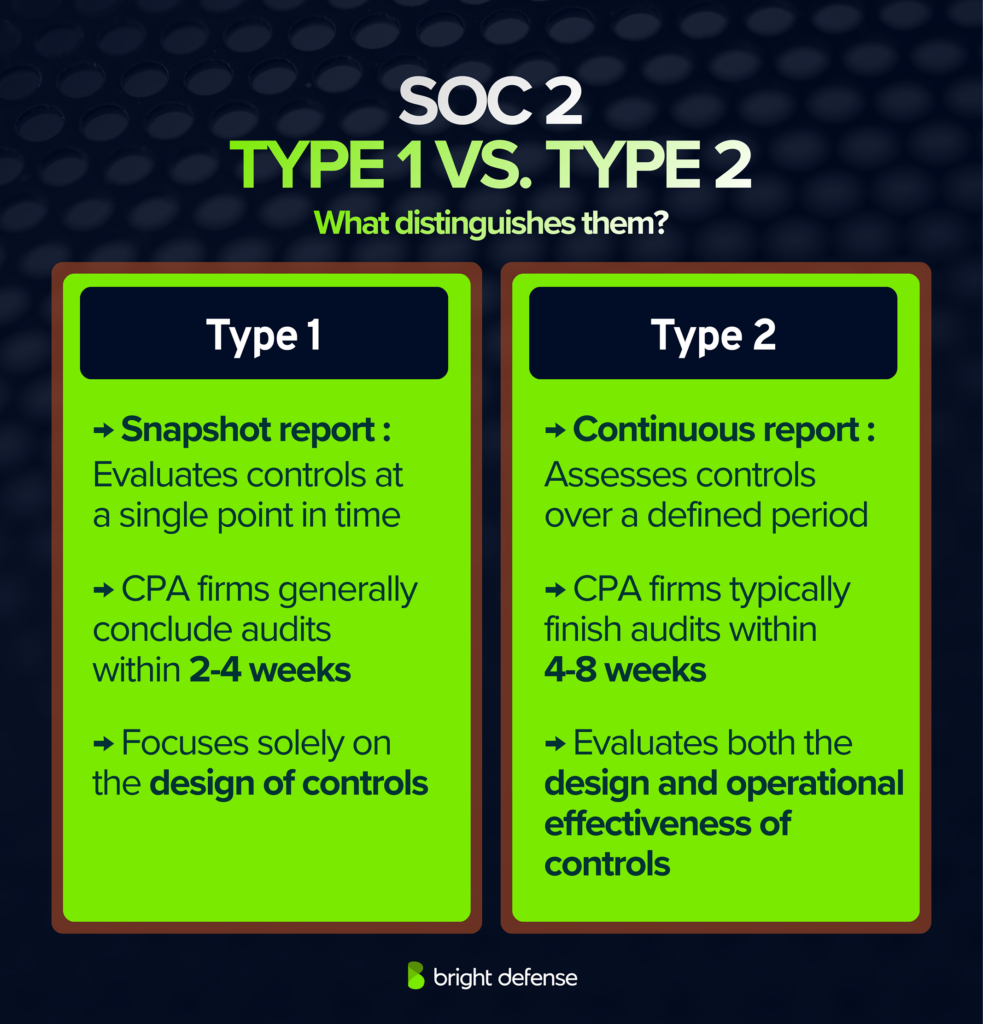
Unlike a Type I report, which examines control design at a single point in time, a Type II report covers several months to confirm the controls functioned consistently in daily operations.
How Does SOC 2 Type II Differentiate From SOC 2 Type I?
SOC 2 Type II differs from SOC 2 Type I in the depth and duration of the audit. A SOC 2 Type I report evaluates whether a company’s security controls are properly designed at a specific point in time.

A SOC 2 Type II report goes further and tests whether those same controls operated effectively over a defined period, often three to twelve months. The auditor examines evidence such as logs, tickets, and access records to confirm the controls were consistently followed.
This extended testing period gives customers greater confidence that the company maintains reliable data protection practices in daily operations, not just in documented design.
What Does A SOC 2 Type 2 Report Cover?
A SOC 2 Type 2 report covers a service provider’s controls for protecting customer data and shows whether those controls worked reliably during a defined review period.

The audit uses the AICPA Trust Services Criteria, with Security always included and optional coverage for Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy depending on what the company promises customers.
A typical Type 2 report package includes management’s written assertion, a description of the system in scope, the independent auditor’s opinion, and detailed tests of controls with the results.
It focuses on the following areas:
- Trust Services Criteria: Security is required, with optional coverage for Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy.
- Report Components: Management’s assertion, system description, auditor’s opinion, and detailed test results.
- Infrastructure: The hosting environment and core technology stack, such as cloud services, servers, networks, and facilities that run the service.
- Software: The production applications and supporting tools, such as operating systems, databases, logging and monitoring, and access management components.
- People: The teams and roles that build, run, and secure the system, plus how responsibilities and access approvals work.
- Data: The types of data the system stores or processes, where it flows, and key protections such as encryption and retention or deletion rules.
- Procedures: The repeatable processes that keep controls working, such as change management, incident response, backups, vulnerability management, and periodic access reviews.
Who Needs A SOC 2 Type II Report?
A SOC 2 Type II report is typically needed by service providers that handle customer data and must prove, through an independent audit, that their controls operated effectively over a defined review period.

SOC 2 reports support assurance needs for both the organization and its customers, covering controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
A Type II report is common in formal procurement and vendor risk reviews because it shows ongoing control performance over time, not only control design at a point in time.
- SaaS companies that host customer data and sell to mid market or enterprise buyers often need a Type II report for vendor security reviews.
- Cloud service providers and cloud platforms often need a Type II report to show control operation across the audit period.
- Managed service providers and outsourced IT operators often need a Type II report when they administer customer environments or security tooling.
- Data hosting, data analytics, and data processing vendors often need a Type II report when they store, process, or transmit sensitive customer information.
- B2B vendors that integrate with customer systems often need a Type II report when customers evaluate access controls, change management, and incident response.
What are the Benefits of SOC 2 Type II?
SOC 2 Type II compliance can offer several meaningful benefits for your organization, from building customer trust to supporting smoother vendor reviews.
The list below highlights potential advantages your organization may experience after achieving SOC 2 Type II compliance:
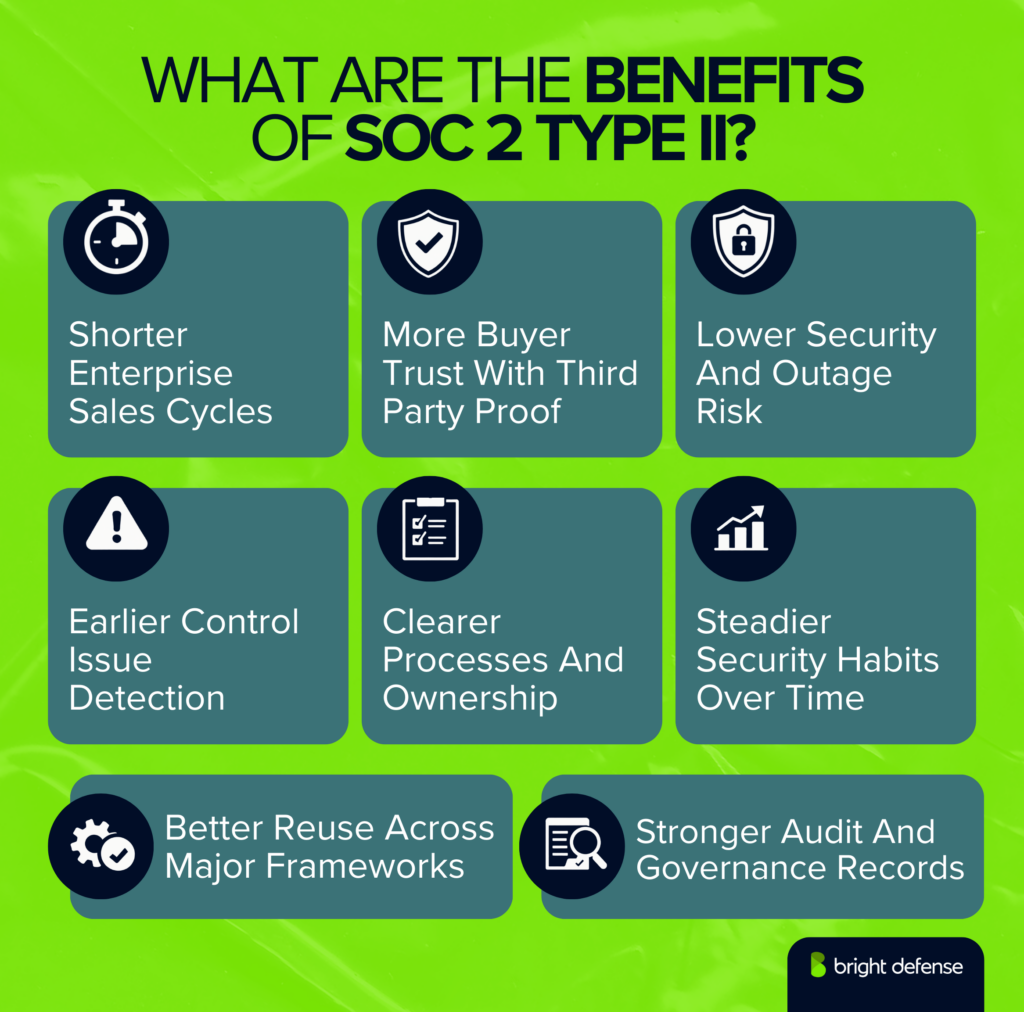
1. Customer Trust and Reputation
75% of consumers say they will not buy from companies they do not trust with their data. Stakeholders increasingly expect verifiable evidence of data protection capabilities. A SOC 2 Type 2 report provides independent, third-party validation that security practices meet established standards over time.
This external assurance builds customer confidence and safeguards organizational reputation, especially critical when data breaches can inflict millions in damages and lasting brand harm.
2. Market Access and Procurement Readiness
85% of enterprise buyers require SOC 2 reports before signing contracts, making Type 2 attestation a critical prerequisite for vendor consideration. Organizations with current reports gain immediate competitive advantages, shortening sales cycles from months to weeks.
This certification enables smaller firms to compete for contracts with large enterprises and regulated industries that would otherwise be inaccessible, directly expanding addressable market opportunities.
3. Lower Security & Outage Risk
SOC 2 Type 2 fieldwork tests control design and operating effectiveness across the Trust Services Criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. This validates whether protections work in real conditions over time.
Organizations must demonstrate that encryption, access controls, intrusion detection, logging, and disaster recovery operate consistently during the review period, surfacing weaknesses before they escalate into incidents or outages.
IBM’s 2025 Cost of a Data Breach research reports the global average breach cost reached $4.44 million, demonstrating how stronger day-to-day controls can significantly reduce financial and operational exposure.
4. Early Threat Detection Through Continuous Control Testing
SOC 2 Type 2 requires controls to be tested over a defined period, establishing an expectation for continuous monitoring rather than point-in-time checks.
Ongoing log review, access testing, and evidence collection help teams spot control failures and correct them before attackers can exploit vulnerabilities.
This shifts the focus from reactive incident response to proactive risk management.
The business case is compelling: industry pricing surveys place SOC 2 Type 2 compliance costs in the $20,000 to $80,000 range for many small to midsize organizations, while IBM reports the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.44 million. Prevention spending remains modest compared to potential breach losses.
5. Leveraging SOC 2 for Faster Multi-Framework Compliance
Achieving SOC 2 Type 2 compliance builds repeatable security habits because auditors test control performance across a defined review window, typically 3 to 12 months, measuring effectiveness over time rather than at a single point. This sustained testing creates institutional knowledge and control evidence that translates directly to other compliance efforts.
The AICPA provides mapping resources between the Trust Services Criteria and other frameworks, with practitioners citing roughly 80% overlap between SOC 2 and ISO 27001. Additionally, SOC 2 control language commonly aligns with requirements across HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, FISMA, and NIST 800-171.
This allows teams to reuse the same policies, evidence, and control testing across multiple compliance efforts. ISO-focused consulting firms report that starting ISO 27001 from an existing SOC 2 report can cut a month or more from a typical certification timeline, significantly reducing duplicated work and shortening follow-on compliance timelines.
6. Catching Security Gaps Before Attackers Do
Google Cloud’s Mandiant M-Trends 2024 reports a global median attacker dwell time of 10 days, demonstrating that intruders often remain undetected long enough to cause significant damage.
SOC 2 Type 2 assessments counter this risk by reviewing controls across an extended period, making monitoring, evidence checks, and repeat testing part of routine operations rather than one-time activities.
This continuous approach helps teams spot control drift sooner and keep security practices current as threats evolve.
7. Governance Clarity Through Audit-Ready Reporting Transparency
Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report found third-party involvement in breaches doubled to 30%, underscoring the growing role of vendor risk in real-world incidents.
SOC 2 reports provide detailed documentation of controls, testing methods, and auditor findings, giving management a clear view of how security measures operate in practice.
This level of transparency enables leadership to assess risk exposure, review vendor oversight, and refine governance structures based on concrete evidence rather than assumptions.
Ultimately, detailed SOC 2 reporting supports informed decision-making across technical, operational, and executive teams.
8. Building Stronger Security Practices
Preparing for a SOC 2 Type 2 audit drives organizational maturity through formalized policies, clear control ownership, and consistent staff training. These foundational practices translate directly into measurable security improvements.
Microsoft reports multi-factor authentication can block over 99.9% of account attacks, demonstrating how pairing single sign-on with MFA materially lowers the risk of unauthorized access.
Similarly, Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report found the human element contributed to 68% of breaches, underscoring why regular training and clearly documented incident response processes are critical for preventing everyday mistakes from escalating into security events.

What Does A SOC 2 Type II Audit Checklist Cover?
A SOC 2 Type II audit checklist covers the systems in scope and confirms that required controls operated as intended throughout the audit period across your own systems. The most important areas include the following.

- Scope And System Description: in-scope services, system boundaries, locations, system resources, and audit period.
- Trust Services Criteria: Security as the baseline, with other criteria included when applicable under the trust service principles.
- Risk Assessment: documented risks and how appropriate safeguards address them.
- Access Controls: user provisioning, authentication, privileged access, and periodic reviews tied to customers internal controls.
- Change Management: development controls, approvals, testing, and deployment practices that support the organization’s internal controls.
- Security Monitoring And Incident Response: logging, alerting, incident handling, and response records within the security program.
- Data Protection: encryption, data handling, retention, and disposal practices that show the company safeguards customer data and protect sensitive data, including sensitive data.
- Vendor Management: third party oversight, third party vendors, and subservice organization treatment, including cloud computing providers and cloud computing vendors.
- Business Continuity And Disaster Recovery: continuity planning, backup processes, and recovery testing.
- Audit Evidence And Reporting: control evidence, testing results, and management assertions that the audit process involves support for a formal audit.
How Much Does A SOC 2 Type 2 Audit Cost?
A SOC 2 Type 2 audit typically costs between $7,000 and $100,000 in auditor fees, with most small to mid sized companies spending closer to $20,000 to $60,000 and first year total costs often reaching $30,000 to $150,000 after preparation work, tools, and internal labor.

Budget planning becomes clearer when costs are grouped into practical categories that reflect how SOC 2 Type 2 audits operate over time.
- Auditor Fees For The Type II Report: Auditor fees vary based on scope, system complexity, and review period length. Market ranges commonly place the audit engagement between $7,000 and $100,000, with many organizations clustering in the $20,000 to $60,000 range for a standard Type II report.
- Readiness Or Gap Assessment: Many organizations pay separately for a readiness or gap review during the first year. This cost covers an external review of control design and evidence quality before formal fieldwork begins and can materially increase the total budget when outside validation is requested.
- Remediation And Required Security Work: Costs increase when teams need to close control gaps during the observation period. Common drivers include missing policies, inconsistent access reviews, incomplete change records, weak logging coverage, or undocumented procedures that require remediation and fresh evidence.
- Tooling And Vendor Support: Compliance platforms, monitoring tools, ticketing integrations, and advisory services usually fall outside the auditor contract. Subscription fees and consulting support often push first year spending higher, especially when new tooling is introduced to support sustained evidence collection.
- Internal Time And Opportunity Cost: Internal effort represents a significant portion of total cost. Security, IT, engineering, and HR teams contribute time across several months because Type II audits depend on continuous control execution rather than a one time documentation effort.

How Long Is A SOC 2 Type 2 Report Valid?
A SOC 2 Type 2 report remains valid indefinitely, but most customers consider it current for approximately 12 months after issuance or after the end of the report period.

The report documents control performance during a defined review window, so reviewers focus on the report end date to assess how recently the controls were tested.
Organizations typically plan annual Type II audits to meet customer expectations for current assurance and to avoid delays during vendor security reviews.
Frequently Asked Questions About SOC 2 Type II Reports and Related Standards
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) uses Arabic numerals, meaning the technically correct term is “SOC 2 Type 2” under the service organization control framework.
However, many audit firms and older documentation still use Roman numerals, so “SOC 2 Type II” remains widely used in the audit process. To reflect common search behavior and industry usage, some blogs include both terms.
They refer to the same report type.
Both SOC 2 and SOC 3 are based on the same Trust Services Criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy, often grouped as the relevant trust principles.
SOC 2 Type 2 is a detailed, confidential report.
It includes management’s description of the system, control testing procedures, and the auditor’s results from a licensed cpa firm. It is typically shared under NDA.
SOC 3 is a high-level summary of the SOC 2 results. It is designed for public distribution and does not include detailed testing information.
SOC 3 is essentially a public-facing summary of a SOC 2 examination and its resulting report.
Implementing SOC 2 Type 2 generally follows these structured steps:
– Establish your objectives and define how you handle client data.
– Choose an independent CPA auditor.
– Decide on the report type (Type 2 in this case).
– Define your audit scope and applicable Trust Services Criteria.
– Perform a gap analysis to identify missing controls and document existing controls.
– Remediate gaps and implement required policies, internal security controls, and physical access controls.
– Conduct a readiness assessment or mock audit if needed.
– Complete the formal Type 2 audit over a defined monitoring period, with annual audits common for renewals.
For Type 2, auditors test the operating effectiveness of controls throughout the review period before issuing their opinion, including controls tied to system processing and the internal control environment that help protect sensitive data.
These reports serve different purposes:
– SOC 1 focuses on controls related to financial reporting. It is used when a service organization may impact a client’s financial statements.
– SOC 2 evaluates controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
– SOC 3 covers the same criteria as SOC 2 but provides a summarized version for public sharing.
– SOC 1 is financial reporting focused.
– SOC 2 is operational and data security focused.
– SOC 3 is a public summary of SOC 2.
ISO 27001 is a formal certification. An accredited certification body audits your Information Security Management System (ISMS) and, if successful, grants certification.
SOC 2 Type 2 is not a certification. It is an attestation report issued by a CPA firm that evaluates whether your controls are designed properly and operate effectively over time.
Key differences:
– ISO 27001 requires adherence to a defined standard and Annex A controls.
– SOC 2 allows flexibility in control design as long as Trust Services Criteria are met.
– ISO 27001 results in certification.
– SOC 2 results in an attestation report.
– SOC 2 is more commonly requested in North America. ISO 27001 is globally recognized.
PCI DSS is a payment card industry standard that applies specifically to organizations that store, process, or transmit cardholder data. It contains 12 prescriptive requirements and must be validated either through a Qualified Security Assessor audit or a self-assessment questionnaire, depending on transaction volume.
SOC 2 Type 2 applies to any service organization handling customer data and evaluates controls against the Trust Services Criteria. It requires an external audit by a CPA firm.
The main differences:
– PCI DSS focuses strictly on payment card data.
– SOC 2 covers a broader range of customer data and operational controls.
– PCI DSS compliance is required to process card payments.
– SOC 2 is typically driven by customer and contractual requirements.
Yes. SOC 2 was developed in the United States by the AICPA, but it is increasingly used globally. European technology companies, SaaS providers, and cloud vendors often pursue SOC 2 when selling into the U.S. market or working with North American enterprise customers.
However, ISO 27001 remains more widely recognized across Europe. Many European companies maintain ISO 27001 certification and obtain SOC 2 to meet U.S. client expectations.
SOC 2 is based on the Trust Services Criteria defined by the AICPA. The five principles are:
– Security – Protection against unauthorized access (mandatory in every SOC 2 report)
– Availability – Systems are available as agreed in service commitments
– Processing Integrity – Processing is complete, valid, accurate, and timely
– Confidentiality – Sensitive information is protected from unauthorized disclosure
– Privacy – Personal information is handled according to stated privacy commitments
Security is mandatory. The other four are optional depending on scope.
Yes. SOC 2 is widely regarded as a cybersecurity audit. It evaluates whether an organization has properly designed and implemented controls to protect systems and customer data.
However, it is broader than just technical security testing. It also assesses governance, policies, documentation, and operational processes across the Trust Services Criteria.
A SOC 2 Type 2 report covers a defined review period, typically 3 to 12 months.
The report does not technically expire. However, most customers expect a report issued within the last 12 months. As a result, organizations typically complete a new SOC 2 audit annually.
SOC 2 is voluntary but commonly required for service organizations that handle customer data.
This typically includes:
– SaaS companies
– Cloud service providers
– Managed service providers
– Data centers
– IT and technology vendors
– Financial technology providers
– Healthcare technology vendors
Enterprise customers frequently require SOC 2 reports during vendor risk assessments.
SOC 2 does not specifically mention artificial intelligence.
However, if AI systems process, store, or transmit customer data, they fall within scope of the Trust Services Criteria. The same requirements for security, confidentiality, privacy, and availability apply to AI systems as to any other system in the environment.
SOC 2 governs how AI systems are controlled, not how algorithms are designed.
There is no formal pass or fail result.
If significant control deficiencies are identified, the auditor may issue a modified, qualified, adverse, or disclaimer opinion. These opinions describe weaknesses in control design or operating effectiveness.
So while you cannot technically “fail,” you can receive an unfavorable audit opinion.
SOC 1 focuses on internal controls relevant to financial reporting. It is used when a service organization’s systems impact a customer’s financial statements.
SOC 3 covers the same Trust Services Criteria as SOC 2 but provides a high-level public summary. It does not include detailed testing results and can be shared publicly.
SOC 1 is financial-reporting focused.
SOC 3 is a public-facing security summary report.
Yes.
Healthcare organizations, especially those providing software or processing patient data, often pursue SOC 2 to demonstrate strong security and operational controls.
However, SOC 2 does not replace HIPAA. Healthcare entities in the United States must still comply with HIPAA if they handle protected health information.
SOC 2 complements healthcare regulations by validating broader security and control practices.
A SOC 2 Type I report evaluates whether your company’s internal controls are properly designed at a specific point in time within the control environment. It is a snapshot assessment.
A SOC 2 Type II report evaluates whether those controls are not only designed properly but show design and operating effectiveness over a defined period, typically 3 to 12 months. Because it supports soc 2 compliance and demonstrates ongoing effectiveness, Type II provides stronger assurance and is more commonly requested by customers and enterprise clients.
Get In Touch



